Cap table vs Stock ledger
This article talks about two types of documentation processes that govern equity management in a company – Cap table and Stock ledger.
Equity management is the backbone of every business. Be it hiring top talent in the industry, attracting the right investors, working with the best consultants, or simply elevating the brand value and perception, equity is at the core of it all. Thus equity issuance, tracking, and management are highly specialized tasks. But ever wonder how it is done?
Cap Table vs Stock Ledger
In the early stages of a business, equity management is quite simple. A startup typically operates with a couple of founders and a handful of employees. Equity tracking and stock-related communications are as simple as updating a log on an excel sheet. One person can manually manage this with ease. However, as a business expands and more stakeholders come on board (employees, investors, consultants) with multiple vesting schedules, manual equity management becomes complex. This is when the differences between cap table and stock ledger are prominent and full-time resources must be allocated to maintain them separately. Let’s take a closer look.
What is a cap table?
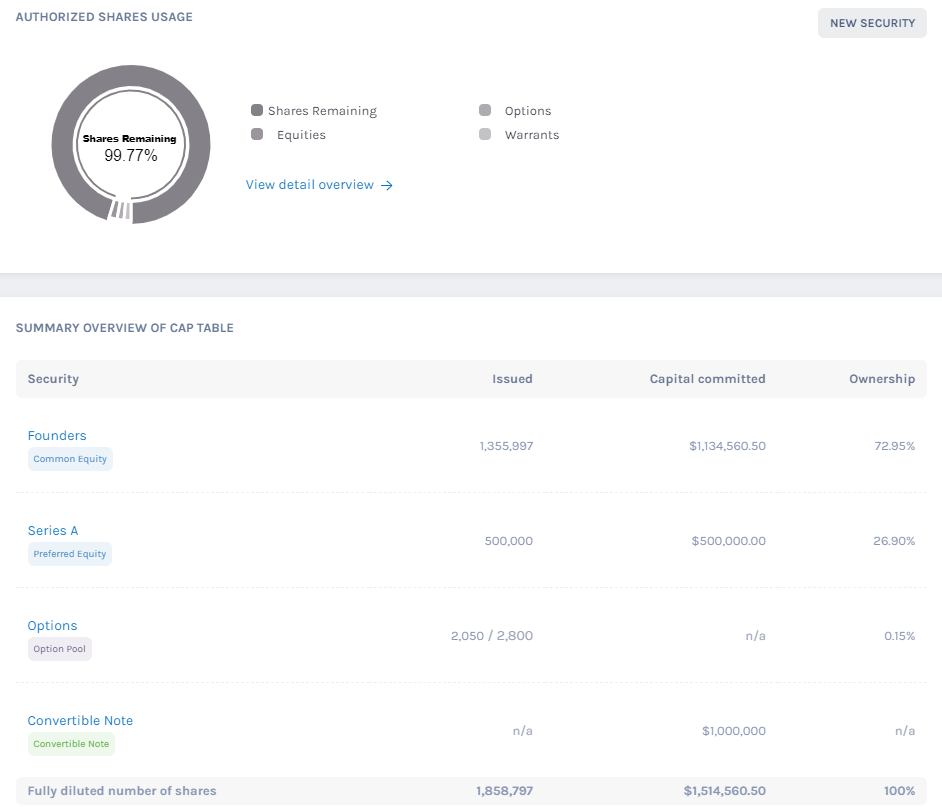
A company cap table is a comprehensive document that summarizes its ownership structure. Though not a legal text, it is crucial reference material for all equity transactions, both internal and external. Thus the true value of a cap table lies in its dynamic nature. It should be up-to-date at all times displaying the current status of who owns how much, irrespective of events that cause changes in the equity structure. Some possible events that impact equity structure are new stock issuance and repurchase in cases of new recruitment, premature shareholder exit, ESOP plans, funding rounds, changes in option pool, etc.
A company cap table template is not fixed. It varies with the needs of the business as well as the operating industry. Though working on spreadsheets has been the traditional approach, opting for cap table software as early as possible is a smart move in the current business scenario. Since cap tables are not just a live compilation of tabulated data, but also an important tool for calculating future equity scenarios using in-built financial models, it is best to automate this process and minimize human error.
Why is a cap table important for a company?
As we see, the company cap table, otherwise known as the ‘capitalization table’, basically breaks down its equity structure in terms of the total number of authorized shares, stocks issued, vesting schedules, and the extent of debt conversion. But what can one do with this information? How is it relevant to the business process? Let’s take a look at the three important functions of a cap table:
- Clarity in voting requirements – One look at a company cap table reveals shareholder classifications. It becomes important for who is holding which type of share. This information in turn reveals their voting rights. Founders can easily reach out to the relevant people to sign off on various management decisions.
- Funding rounds – One of the primary things investors demand during a finance round is the company’s updated cap table. Based on this information, investors understand company valuation and predict the impact of new funds on the equity structure. The best investors in the industry do not work with companies that have an unreliable history of cap table management. Besides, an updated cap table works in favor of the founder as well. They can enter an investment round with much clarity about how much equity they can part with and at what cost.
- Build finance scenarios – If a company works with the right cap table template suited for their business, information from this document can be easily used to create financial models, such as waterfall analysis and round modeling. These models help founders track their progress with exit scenarios in mind. Such information helps businesses recognize faults in strategies and adopt corrective actions as early as possible.
What is a stock ledger?
A stock ledger is also a comprehensive document that captures details of company shareholdings. But unlike a cap table, a stock ledger does not summarize the present ownership structure. A stock ledger template is designed to document all shareholder information from the inception of a company. It is an archive for all equity transactions ever since the company started to issue shares. Stock ledgers are typically internal records produced only by legal authorities in case of audits.
In the initial stages of a business, when the volume of equity transactions is low, a stock ledger is maintained by the Corporate Secretary as part of the company’s minute book. As the company expands and the equity structure begins to change (multiple issuances, transfers, and cancellations) stock ledger maintenance no longer remains a one-person job. This process now has to be entrusted to a third party called Stock Transfer Agents. Then on, transfer agents take up complete responsibility starting with stock issuance to stock ledger maintenance.
Why is a stock ledger important for a company?
A stock ledger is a legal requirement for all public and private companies. Though their obligations vary, no company can run a legal business without maintaining a proper stock ledger. Irrespective of the formats used for a stock ledger template, here are the two important functions of a stock ledger:
- Optimum governance – Based on the classes of shares held, shareholders are in many ways the real owners of a company. The management cannot implement important decisions without the consent of shareholders. Thus a stock ledger is a go-to document to have clarity on which shareholders are entitled to during the life of a company as well as in exit scenarios. Without the historical equity transaction data provided by stock ledgers, optimum governance of a company is impossible.
- Audits – Audits are an integral part of operating a successful business. Stronger the audit reports, the better the stability and reputation of a company. One of the basic demands from a company during a regulatory or tax audit is the presentation of an up-to-date stock ledger. This document provides clarity about all equity transactions and their ownership details. Analyzing this document is the quickest way to identify any foul play by the company and the shareholders.
What is the difference between a stock ledger and a cap table?
Since both these documents record shareholder information, it is an easy mistake to consider them to be interchangeable.
A stock ledger and a cap table are ultimately instruments that record shareholder information. One may assume both to be the same. Maybe in the early stages of a business, this could be true. But for a mature company, the difference between cap table and stock ledger is well pronounced. Here are the two basic points of divergence:
- Recorded Data – A cap table is a live document and summarizes the present ownership structure of a company, relevant shareholder details, as well as the options pool. Cap tables maintained on excel sheets have a time lag just enough for a manual update. But with cap table software, even this delay can be minimized. Irrespective of events that impact the equity structure, a cap table always displays current equity ownership information. A stock ledger on the other hand is an up-to-date archive of all equity transactions along with information of all shareholders of the company since the issuance of the first share.
- Scope – A cap table template is designed in a way that not only does it benefit the company, but also it is easily understood by external parties such as investors. Thus the scope of a cap table is not limited to internal purposes alone. Cap tables are one of the first documents investors want to see during finance rounds. Besides this, information from a cap table lends to various financial models that enable founders as well as investors to analyze the company’s present valuation, future potential, and predict the impact of new money on the current equity structure. Meanwhile, a stock ledger template is designed to document past and present equity transactions along with details of shareholders involved in these deals. Stock ledgers do not reflect the option pool. Neither can data from this document be used for any financial modeling processes.
General Structure of Cap Table and Stock Ledger
Now that we know the basic differences between a cap table vs stock ledger, let’s explore the general structure of these documents. Though there are no set formats for these, certain details are standard across all cap tables and stock ledgers. Let’s discuss this one by one.
What is the general structure of a company cap table?
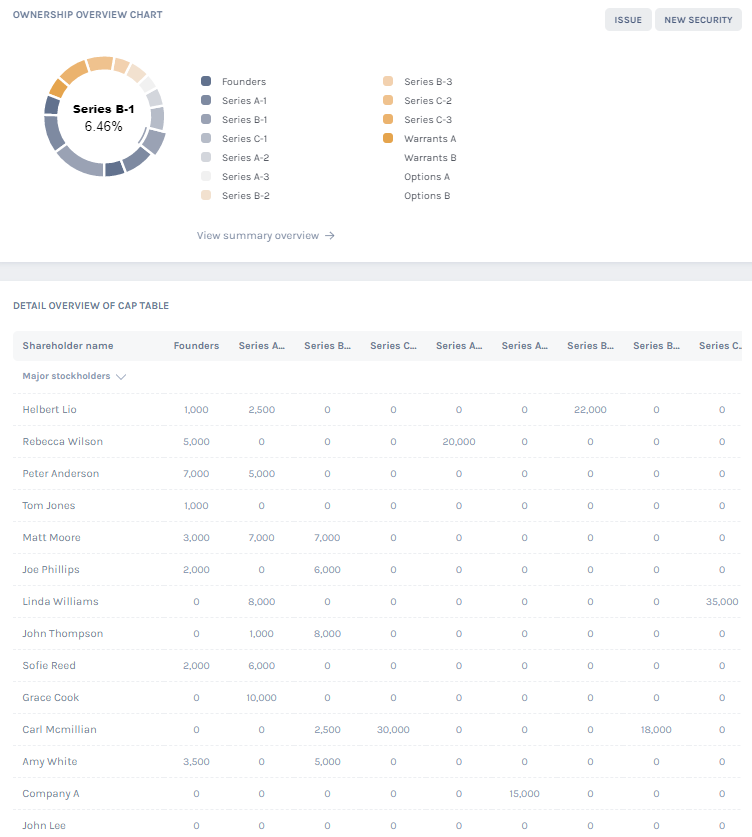
A company cap table structure fundamentally depends on the type of company. A limited liability company’s cap table will have many limited shareholders and equity-related information when compared to a public company with thousands of shareholders. Irrespective of the company type, a typical cap table must include:
- Name of shareholder
- Class of shares held
- Number of shares held
- Details about share acquisition (vesting schedules, strike price, exercise date, expiry date)
- Total number of authorized shares not yet allocated
- Options pool
Cap Table Template and Example
What is the general structure of a company stock ledger?
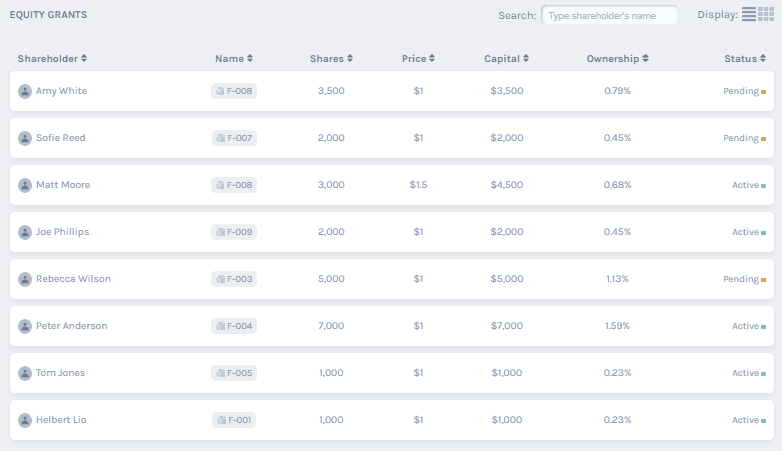
Similar to a cap table, a stock ledger must have a simple structure as well. Since the main purpose of a stock ledger is to provide complete details about all shareholders from the formation of the company, the general structure will vary with the type of business and nature of equity transactions in that particular industry. However, here are the basic parameters that shouldn’t be left out of a stock ledger template:
- Name of the stockholder
- Residential address of stockholder and all other relevant contact details
- Serial number on the stockholder certificate
- Type of stock held
- Total number of stock held
- Date of stock issued
- Date of stock cancellation (in any)
Stock Ledger Template and Example
How cap tables are used?
Now that we know how a company cap table is structured, let’s discuss their application. How can one use this massive chunk of data from a cap table? How does it benefit the company? Here are some possibilities:
- Cap tables help design lucrative ESOP plans that help attract the best talent in the industry.
- Cap table software like Eqvista enables employee access to cap tables. This leads to increased transparency between employers and employees. This, in turn, has a direct impact on employee retention.
- Founders use cap tables to prepare for finance rounds. Among other things, it helps them decide how much equity can be given away.
- Data from cap tables are used for waterfall analysis and round modeling. Stakeholders stand a better chance at exploring possible financial scenarios well in advance.
- Cap table data helps prioritize stakeholder payouts (dividends and in case of sale).
- Cap tables are an important document for taxation and regulatory compliance.
How is a stock ledger used?
Similarly, how does a stock ledger template help in equity management? Here are some direct applications of a stock ledger:
- Track stock issuance from the first equity distribution
- Track stock transfers
- Track stock repurchases in case of exit or early termination
- Track stock cancellations
- Monitor timely dividend payouts
- One-point reference for the company and stockholders
Manage Your Company Cap Table & Stock Ledger on Eqvista
As we see, managing and updating cap tables is a complex task. Considering the legal repercussions involved in case of lapses in equity management, it is best to automate this process using cap table software as early as possible. Using sophisticated cap table software like Eqvista not only helps manage day-to-day activities involved in a company’s equity management but also aids in creating hybrid cap tables in case of mergers and acquisitions. You can also process your 409a valuation and record your share price on the platform as well. These articles provide a glance into Eqvista’s extensive services. To know more, reach us today.
Interested in issuing & managing shares?
If you want to start issuing and managing shares, Try out our Eqvista App, it is free and all online!
