Corporate Structure – All you need to know
Keep reading to know all about the corporate structure basics and the different corporate structure types.
Of all the decisions that you make when you are starting your business, one of the most important decisions is creating a proper corporate structure for your company. This decision is important as it would impact the way your company runs and how it grows. For instance, have you ever wondered why some companies have CEOs while the others have presidents? Well, that is what we are going to talk about in this article.
Keep reading to know all about the corporate structure basics and the different corporate structure types.
Corporate Structure: Understanding It’s Basics
Let us begin by understanding the basics. Presidents, vice presidents, CEOs and CFOs – what is the difference between them? With the changing corporate horizon, it has become very difficult to keep track of what people do and where they stand in the corporate ladder. Should you pay attention to the news related to the vice president or the CFO? What do each one of them do?
To be able to create a corporation in which the interest of the stockholders are looked after, a lot of firms implemented a two-tiered corporate hierarchy. The first tier is made of the board of directors or governors, who are individuals elected by the shareholders of the corporation. And the second tier is the upper management, where the individuals are hired by the board of directors.
Let us start off by understanding the basic parts of a corporate structure and what each of its members do. Also, it is important to note that the structure shared here is what is common in the US and can be different in other parts of the world. But by the end of this, you will get the basic idea about what a corporate structure is.
Corporate Organization Structure
As mentioned above, the corporate structure is a way of running a business. Corporate structures include:
#1 Board of Directors
The board of directors usually report to the shareholders in the company and their tasks include:
- Holding annual meetings
- Protecting shareholders
- Creating committees
- Writing bylaws
- Company compliance
- Reviewing the company’s goals, budgets, and plans
- Keeping the CEO and upper management on track
The board can be just one person or many people from a diverse background. And as mentioned previously, the shareholders elect board members while the company’s bylaws will tell how many members the board needs. Normally, the number of board members is always an odd number to avoid tied votes. Even though the member’s personal assets are separate from the company, they are still responsible for the business debts, the corporation, its employees, agents, officers, and subsidiaries.
The directors in the company may include:
- Chairman: This is known as the main person who leads the business and is responsible for the actions of the board. The person would work with the top officers in the company to keep the process going. They also act as the public face of the company.
- Inside Directors: The inside directors, also called executive directors, are the ones who are in charge of the company’s budget. They may be shareholders or top managers.
- Outside Directors: The outside directors have the same responsibilities as the inside directors, but they are not the company’s managers or officers. They offer unbiased opinions.
#2 Corporate Officers/Management Team
Corporate officers are a part of the upper management team of the company and are chosen by the board. These officers handle day-to-day tasks and look out for the interest of the company. There are four kinds of officers in a company:
- President or CEO: This officer works with the board of directors, signs documents, and enforces policy in the company. They may also be the president.
- Vice President or Chief Operations Officer (COO): This person is the senior executive in the company. COOs run the daily business, sales, products, marketing, and staff. The VPs normally replace the president if they are no longer acting in this capacity.
- Treasurer or Chief Financial Officer (CFO): This person is in charge of the finances in the company. A CFO writes budgets, reports, and tracks the spending in the company. Most CFOs give reports to the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), the board, and other government agencies.
- Secretary: This officer keeps records, minutes, and the books.
#3 Shareholders
From the name it is understood that the shareholders own the company. These people do not normally take part in the daily business of the company, especially if they are made up of investment firms for larger corporations. And the number of shareholders in the company is based on the business entity structure. For instance, an S corporation normally has fewer than 100 shareholders and C corporations have more than that.
Since each shareholder holds a part of the company, owning more of the business gives that shareholder more power. Shareholders typically own the common stock shares in the company, and are not personally liable for the company but do help in making some decisions. And even though the corporation’s owners are its first shareholders, larger companies can have many public shareholders.
The shareholders in the company have the rights to vote on:
- Disposing of assets
- Dissolving or merging the company with another
- Changing the Articles of Incorporation or the bylaws
- Choosing the members of the board of directors
Special Considerations
Even though the normal corporate structure has been described, there are some special cases. To begin with, the management and the board of directors have the same goal of maximizing share value. In theory, the management handles the daily operations while the board ensures the shareholders are adequately represented. But in reality, many boards include members of the management team.
Why is Corporate Structure Important?
Corporate structure separates the managers and the owners of the company. It is important to have a solid structure as it can grow a small family business into an MNC (Multi national corporation). A proper corporate structure helps a company share its goals and outline the responsibility and roles. A business needs a structure to be profitable and grow, and it’s also monumental for attracting investors for your company.
Here are some of the reasons why a corporate structure is important in a company:
- Structure Allows for Better Communication: For a company to be successful, the flow of information has to be smooth. The structure will help people have clear lines of communication in mind. Everyone will know what they need to share with whom.
- Clear Reporting Relationships: The reporting relationships also need to be clear so that every member knows what their responsibility is in the company and who they are accountable to. If this is not done, the task might fall through the cracks which can affect the success in the company. Additionally, a clear relationship also helps managers supervise those below them and the employees know who they can turn to for help or direction.
- Expansion & Growth: Proper corporate structure can help the tasks to be done in a better way. This in turn can help the company succeed and grow. Without a proper structure, there would be weak spots in a company which would hinder company growth and expansion.
- Fit’s Company’s Needs: Different industry companies have different mixes of talents, so it’s important to manage the functions properly. This is done with a well-defined corporate structure. For example, in a software company, there is a large team of development staff. Structuring the reporting relationships in the team can help increase productivity, creativity and the deadlines are met. All this is important for the company’s success.
- Efficient Task Completion: In continuation to the previous point, with a proper corporate structure, the projects and tasks would be completed on time and with the best quality as everyone knows what their roles are and what they are accountable for. In short, deadlines and quality requirements are met in this case.
Corporate Share Structure
Corporate share structure is the establishment of shares of one or more types in a company and the issuance of some or all those shares to the shareholders. In short, the type of shares that are created and issued is the corporate share structure for that company. And even though the share structure changes in the company, it is always beneficial to start off the corporation on the right footing.
To explain more, a company needs to have at least one class of shares which can have one or more series of shares if the special rights and restrictions connected to the class are created.
For example, let us say that company XYZ has Class A preference shares that have about 10,000 shares in it with no restrictions or rights attached. Now, the same company can also have another class of shares, Class B preference shares with 500 shares in it and voting restrictions. There can be any number of classes in the corporate share structure in a company. These different types of shares issued are deemed the “classes of shares”. It is also called the capital share structure. Basically, shareholders can hold the same classes of shares just like other shareholders or even hold more than one class of shares in a company. In short, there are no limits to the number of different share classes a company can have.
Corporate share structure classes
There are three kinds of share structures that a company can have. One is the simple single class share structure where all the shares have the same rights and restrictions. But for more complex share holdings, here are two more share structures, as below:
- Dual-Class Share Structure: This structure divides the voting rights and the profit-sharing rights. And it in turn offers the founders and management with more voting power as compared to the ordinary shareholders in the company. Due to this, the founders can easily enjoy the following benefits in the company:
- Founders can focus on the innovation and growth of the company without any interference from the shareholders.
- The owners that have a long-term view for the business would be protected from the urge from the investors and other shareholders to focus on short-term gains.
- This structure guards the founders against takeovers, mostly when the company becomes public.
- Multi-Class Share Structure: A multi-class corporate share structure is when a company has more than two classes of shares. This is the most favored share structure that many companies follow as it helps the company evolve better as per the needs of the business.
A company just needs to create the corporate share structure most suitable for its amount and types of shareholders. It should also be able to differentiate between the founders and the shareholders in the company so that each gets what they deserve from the company.
Eqvista Cap Table Software
Eqvista is a cap table management software that allows you to record all the shares in your company while you track and manage them. It would also help you understand the corporate share structure of your company. You can use the application to record your share structure. It is an efficient and cost effective way to handle the cap table and manage the shares of the company.
When you use Eqvista, you will be able to manage all the shares in the company and the share structure easily. It will also help you keep track and avoid any errors that many lead to forensic audits later on. In case something out of place is added in Eqvista, it would have you correct the error before processing the transaction.
Here are some of the key advantages of the Eqvista software:
- It would assist you in filing your company with your Division of Corporations of your state.
- The management of the cap table would display a clear provenance record.
- All the shares of your company would be handled by Eqvista in a transparent manner.
- It would reduce manual work and eliminates the need to rely on third party databases.
- A direct communication link would be set between investors and the issuers.
- Eqvista would accurately calculate the corporate items like share issuances and vesting schedules.
- The software is free to use (for smaller companies).
Corporate Structure Examples
Let us get back and talk about the corporate structure types. Among the types of organizational structures, two of them stand out, with the first one presenting 3 subtypes. Each of them have been explained in detail below with an example to help you understand it better.
#1 Line, functional and line-and-staff structures
This is the first type that has three subtypes in it. Each of these are explained below in detail.
Organizational structure example – Line
The line corporate structure has the CEO or president at the top. It is then followed by the VPs or directors for specific areas. After that comes the managers and so on. This structure can be seen below:
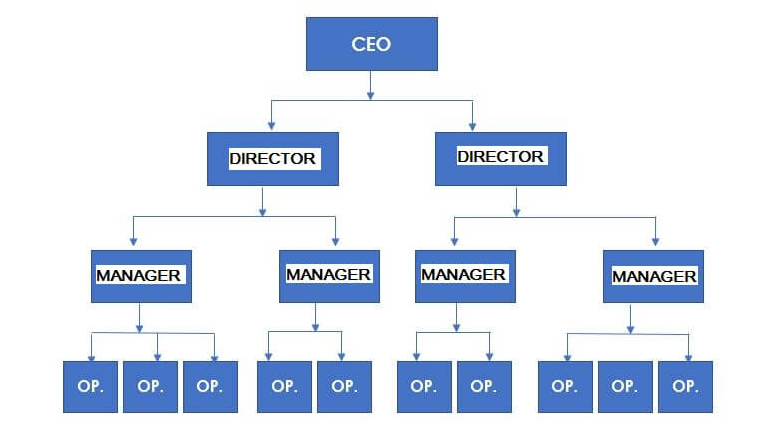
This is a very rigid structure that has little information exchange. It is normally used in bureaucratic companies in which there is little collaboration. These days, this structure is not used as it was in the past for academic, religious and military organizations. In this basically one area does not interfere with the work of the other and staff only obey the order of their superiors.
Organizational structure example – Functional
This structure comes from the line structure. The only difference is that the employees in an area need to report to all the directors.
For instance, an employee in the development team is called by the HR manager to handle a matter in this area. The development team manager can do the same by calling the same employee. This helps to avoid excessive specialization and centralization in tasks in your area. This is how the hierarchy looks like:
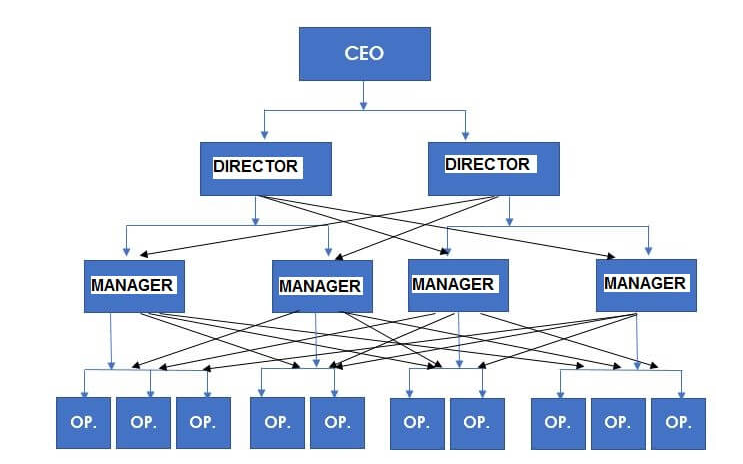
In the world today, this is the most used corporate structure in many companies. Everything here depends on the relationship between managers to aid the internal communication.
This structure is great for small companies where informal structures allow functional control over employees without generating conflicts between managers.
Organizational structure example – Line-and-staff
This is the same as the line corporate structure just that the staff advises, authorizes, makes reports, gives opinions and supports the organization.
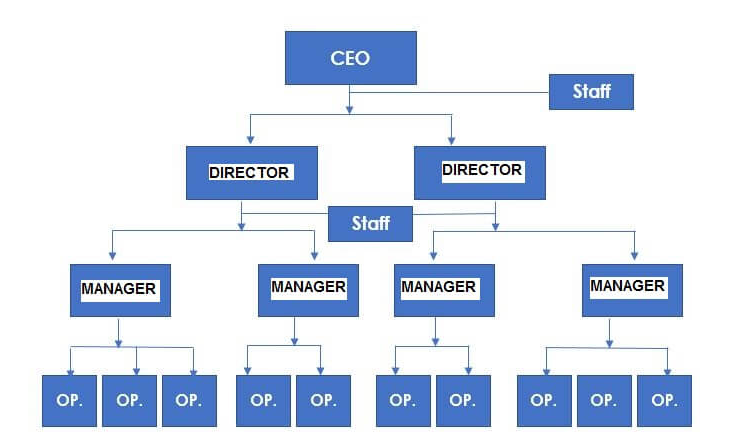
This structure is normally used in law firms, engineering firms, insurance companies, regulatory agencies, etc.
In short, it is used in companies that need isolated technical advice to assist employees who manage or handle the daily operations on the front line.
#2 Project-based Structures
This corporate structure is used for highly dynamic and creative companies such as the special industrial equipment installation projects companies, architecture firms, software companies, and event organization companies. It has a series of specialized employees that gather a work team as needed. And for each project, the collaborators report to a different leader. As soon as the project is done, the manager assigned them another project and leader.
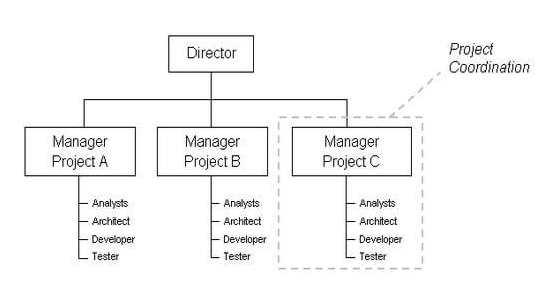
Conclusion
In the end, it is important to know everything about the corporate structure and its types. It would help you choose the right structure for your business which eventually helps it in growing and succeeding. And while you focus on these things, remember that you need to keep a track of all the shares you are giving out. Eqvista can help you with it. Click here to learn more!
Interested in issuing & managing shares?
If you want to start issuing and managing shares, Try out our Eqvista App, it is free and all online!
