Share Certificates in China: Key Considerations for Shareholders and Corporations
If you’re wondering how to understand how share certificates work in China, this article can be the best source.
China’s economy has expanded phenomenally, moving the nation up to the second biggest in the world. Its customer base is quite diverse, spanning industries as varied as manufacturing, IT, banking, and retail. It is crucial for investors and companies doing business in China to have a firm grasp of the main issues surrounding share certificates. Share certificates are an essential part of the business ownership structure.
They are physical representations of the rights and advantages of owning a company’s stock in an organization. To ensure openness and conformity in China’s corporate environment, it is crucial to understand the complexity of share certificates, from issuing and transferring certificates to the privileges and obligations they involve. If you’re wondering how to understand how share certificates work in China or the various types of shares and share certificates, this article can be the best source.
Share certificates in China
A share certificate is a formal piece of paper representing ownership in a company. Shareholders may use this certificate to verify their ownership of a certain number of shares. Share certificates in China, however, merely show the name and number of shares owned by each shareholder.
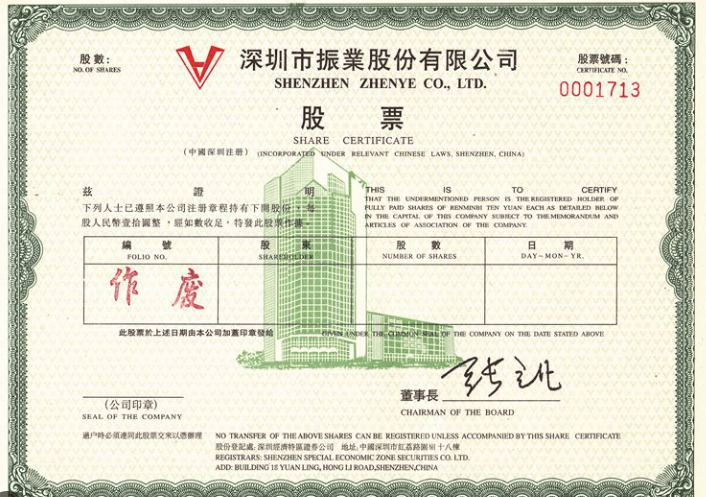
The figure is not indicative of the worth of the investor’s stock. Companies may issue several certificates to shareholders who possess shares in various asset classes, each with unique identifying information. To prevent forgery, all certificate-issuing organizations include complex designs in their documents.
Importance of Share Certificate
Share certificates in China are used primarily for recording the ownership details of each shareholder. It eliminates fake investors by keeping track of legitimate shareholders’ names. To keep up with changes in share ownership, companies must constantly update the information on this certificate.
Take the example of an investor who buys 200 shares of a single firm. A few weeks later, he sold 50 of his shares. He makes a second investment in the same firm by buying another 100 shares. These certificates must accurately represent all transactions. This simplifies auditing and balancing procedures.
Types of shares and share certificates
Depending on the company’s articles of organization, shareholder agreements, or other applicable agreements, preferred and ordinary share certificates in China might have somewhat different features. It is also important to check with legal and financial specialists to get the most up-to-date information since legislation and practices pertaining to share certificates might change over time.
Similarly, the types of shares and share certificates issued to the members vary from company to company. However, the most frequently issued shares are either common or preferred. Let’s understand more about these types in the following section.
Common shares
When investors purchase common shares, they buy a piece of the firm. This stock option grants shareholders voting rights and the ability to elect the company’s board of directors. Investing in common stocks, also known as common shares, may result in significant financial gains. After all other creditors, including stockholders and bondholders, have been paid in full, the company’s common shareholders are entitled to any remaining assets.
Common stock may be issued to an individual during the IPO of a firm. Every share of common stock is recorded in the balance sheet’s shareholder equity section.
Preferred shares
Preferred stock, also known as preference shares, is a stock in which dividends are distributed to shareholders at a rate higher than the rate at which dividends are distributed to holders of common stock. Preferred investors have priority over regular stockholders for the distribution of firm assets in the event of bankruptcy. Common stocks often do not pay a dividend, but preference shares do. Common shareholders often have voting rights, whereas preferred stockholders do not.
Legal Framework of Share Certificates in China;
The People’s Republic of China (PRC) Company Law details the rights and responsibilities of a newly formed corporation. The articles of incorporation or a separate shareholders’ agreement may specify the rights of shareholders and the manner in which they will exercise their rights in voting on certain issues.
Shareholders of a corporation must be included in the company’s official records. If you modify the registered information, you must follow the appropriate amendment processes. In the absence of registration or the completion of registration revision processes, the particulars will not be enforced against an unregistered individual.
The issuing, dealing, and disclosure of securities, including shares, are all governed by the PRC Securities Law. It defines the functions of regulatory agencies like the China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC) and the processes for issuing shares to the public. Share certificates in China may also be subject to the terms of a shareholder agreement or an investment contract. Share ownership, transfer limitations, dispute resolution methods, and other pertinent aspects may be further specified in such agreements.
Share certificate requirements
Share certificates in China are to be issued to shareholders when a firm has been incorporated. There are a few pieces of information that must be included in share certificates in China during the issue as the following.
- The company’s name
- The day when the company was officially formed.
- Capital on record with the government
- Information about the shareholder (including its name, the date, and the amount of their investment)
- The date of verification and issue of the Share certificate and the serial number. The company’s official seal must be affixed to every certificate of capital contribution issued.
In China, company seals are commonly used for legal documentation. The corporate seal or “chop” must appear on share certificates in most jurisdictions. The official business seal guarantees that the document has been properly signed and sealed. The company’s authorized signatories must also sign the stock certificates. These signatories are usually board members, executive officers, or others named in the company’s articles of organization or related resolutions.
Procedures for Issuing Share Certificates In China
Share Certificates in China are issued after a multi-step process. This is a rough summary of the processes required; the specifics will vary depending on the articles of association, relevant rules, and stock exchange regulations.
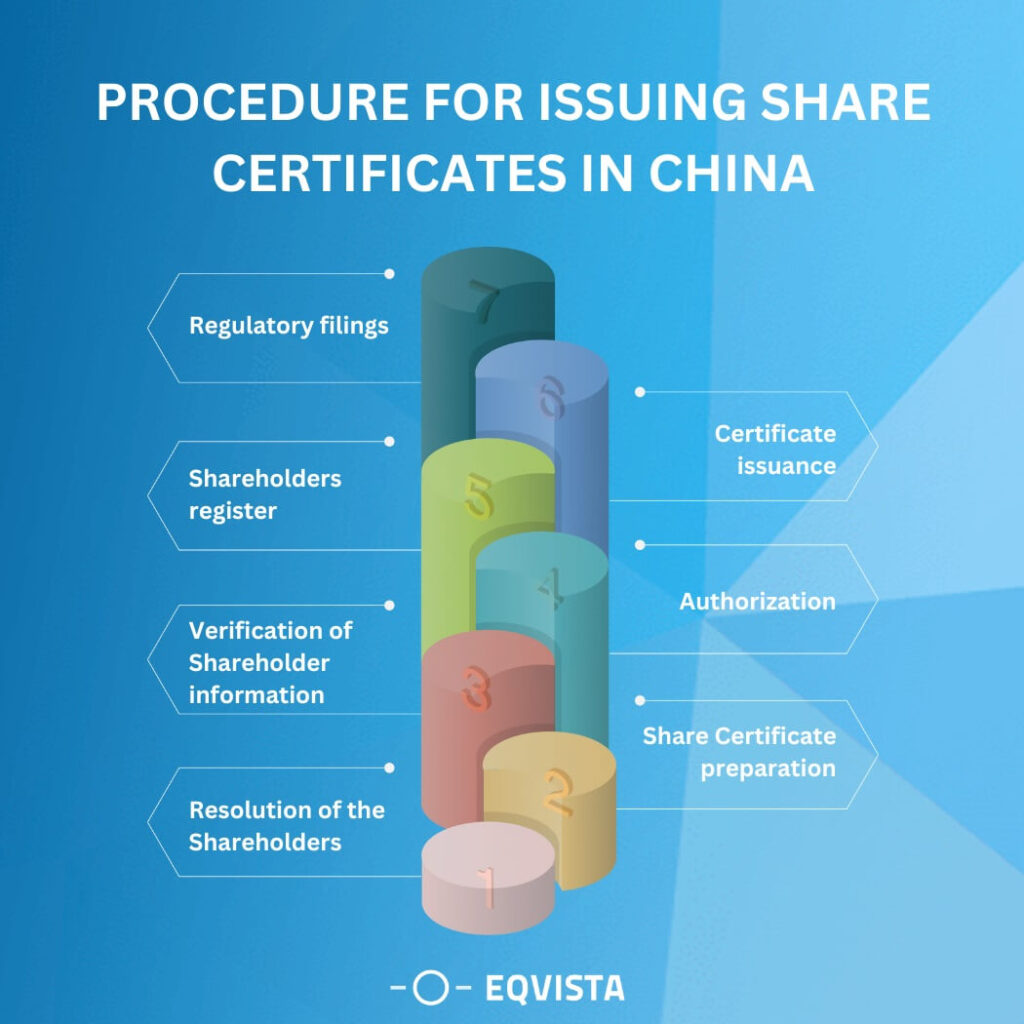
- Resolution of the Shareholders – The issue of stock certificates requires a resolution to be passed by the company’s shareholders. Depending on the procedures established by the company’s internal governance, the shareholders may approve this resolution either in a general meeting or by written consent.
- Share Certificate preparation – Once approved, the business will begin preparing the certificates for the shares. The name of the shareholder, their tax identification number, the number of shares they own, and any other pertinent information must all be included on their respective share certificates.
- Verification of Shareholder information – The corporation makes sure the information on the share certificates is correct by verifying the details shareholders supply. To do so properly, the corporation may have to verify the shareholder’s information against its files and do other due diligence checks.
- Authorization – Certificates of stock ownership are authenticated by the company’s authorized signatories, such as directors or executive officers, and bear the company’s official seal. The certificates of ownership are verified by the company’s official seal.
- Shareholders register – When new stock certificates are issued, they are recorded in the company’s register of shareholders. The register must be up-to-date with the information provided by the share certificates, including the name, address, and number of shares owned by each shareholder.
- Certificate issuance – When the shares have been issued, the certificates are handed to the stockholders. As per the company’s policies, this may include sending the stock certificates to the stockholders’ addresses on file or arranging for their collection.
- Regulatory filings – Additional regulatory filings may be necessary to record the issuing of share certificates in China to the appropriate authorities, which might include the stock exchange or the China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC) if the firm is listed on a stock market.
Record-Keeping and Updating Shareholder Information In Share Certificates:
A shareholder register comprises a public record of the legal and beneficial owners of a company’s shares, including the individuals or entities eligible to vote for the shares, exercise other rights and functions associated with the shares, and collect dividends.
For non-shareholders, access may cost a nominal price but is free for present shareholders. Information about a takeover offer, such as the per-share price, may be communicated to and discussed by shareholders.
The following are the usual stages involved in procedures for keeping the details on share certificates in China relevant and up-to-date about the shareholders:
- The company checks the updated information on shareholders for correctness, including names, addresses, and percentages of ownership.
- The shareholder submits a request in writing, together with any relevant documentation, to have their name and address changed on the share certificates in China.
- The proposal is approved by the board of directors, and a resolution is passed to amend the share certificates.
- If there’s a change in a shareholder’s name, address, or ownership, we need to update the share certificate.
- To ensure the changes are valid, the amendment will be signed by appropriate parties and sealed with the company’s official seal.
Consequences of Non-compliance Of Share Certificates In China
Companies in China risk serious repercussions if they fail to maintain their records up to date and in accordance with local regulations.
- It is possible to face legal repercussions, such as fines and prosecution. Regulatory measures include warnings, limits, and even license revocation.
- Noncompliance might also result in suspending share trading for publicly traded corporations, which can harm their image.
- It is important to remember that failure to comply might slow down corporate expansion via mergers and acquisitions.
To avoid these negative outcomes, businesses should make compliance a top priority by maintaining all necessary records in a timely manner and ensuring that all existing records are correct. Acquiring legal counsel is essential for doing things the right way.
Share transfer and Registration In China
There are regulations to be understood and followed in case of share transfers in China. The Company Law mandates that most shareholders approve a share transfer to someone who isn’t already a shareholder. The transferring shareholder must provide written notice to the other shareholders and get their consent before he may transfer his shares. If those shareholders don’t respond to the written notification within 30 days, they will be assumed to agree to the transfer.
If more than 50% of the other shareholders object to the sale, they must buy the transferred shares. They are presumed to have consented to the transfer if they do not make the transaction.Owners who approve a share transfer have the right of preemption to acquire the shares being transferred at the same price and on the same terms and circumstances as the original owners.
Shares subject to a preemptive right of purchase may be acquired in any proportion agreed upon by two or more shareholders exercising the right. If this is not possible, the shares will be acquired based on the amount of capital each person has contributed.
Experience Eqvista’s Share Certificate Generation Tools!
Share transfer and issuance of share certificates in China require meticulous planning and expert guidance. Failing to adhere to the norms may cause severe legal implications and loss of brand value. To avoid this, you may consider taking advantage of the expertise and service of Eqvista.
Our simplified share certificate generation tools will help you quicken the process. Moreover, we have seasoned professionals who can guide you throughout the journey giving you more time to focus on your core business objectives. Considering a consultation? You can reach us here!
Interested in issuing & managing shares?
If you want to start issuing and managing shares, Try out our Eqvista App, it is free and all online!
