IRS Section 409A
Section 409A is a part of the Internal Revenue Code and governs the non-qualified deferred compensation paid to a service provider of the company.
While many company founders may be unaware of IRS Section 409A, it’s an important tax law that governs the rules for valuing a company’s share price. The law outlines the requirements for 409a valuations as well, hence the name. These would determine how an independent appraiser assesses the value of your company to determine the share price, and ultimately the amount of tax to pay on these.
Despite this, not every company may have a valuation done, especially for those without an Employee Share Ownership Plan (ESOP) or compensation to their shareholders. But if you are about to give shares or options to your employees, then you should know all about IRS Section 409a and the valuation methods. At the end of this article, you will have a better grasp on this.
Let us begin with what the IRS Section 409A is all about.
SECTION 409A IRS
IRS Section 409A is a part of the Internal Revenue Code and governs the non-qualified deferred compensation paid to a service provider of the company. It also imposes a 20% excise tax when the section’s operational and certain design rules are violated. The service providers of IRS Section 409A include the board members, some independent contractors, general employees, and executives. The service providers also include those executives that offer services. For instance, a corporation or an LLC can be a service provider for another company.
Basic of the IRS Section 409A
On January 1st, 2005, IRC Section 409A was added to the IRC (Internal Revenue Code) under Section 885 of the American Jobs Creation Act of 2004. The overall effect of IRS Section 409A is comprehensive due to the broad definition of “deferral of compensation”. In fact, this section was passed based on the practices of the Enron executives who accelerated their payments under their deferred compensation plans to access the company’s funds before it went bankrupt. It was also enacted partly in response to a history of perceived tax-timing abuses due to the limited enforcement of the constructive receipt tax doctrine.
409A DEFERRED COMPENSATION PLANS (NQDC)
According to IRS section 409A, the “non-qualified deferred compensation” has to comply with other rules concerning the distributions and timing of deferrals. So, as per the regulations put up by the IRS Section 409A is applied when there is a “deferral of compensation.” This normally takes place when an employee of a company has a legally binding right during a taxable year to the compensation that would be payable in another tax year or is payable in the current tax year.
IRS Section 409A sets out nonqualified deferral election timing and distribution schedules rules. Nonqualified plans must comply with 409A rules to retain their tax-deferred status.
There are many exceptions to this, which includes welfare benefits such as death benefit plans, disability pay, sick leave, and vacation leave, along with qualified plans such as 401(k) plans and pensions. Some of the other exceptions include ones for “short-term deferrals,” which are the payments made within two and a half months of the year in which the deferred compensation is no longer subject to a substantial risk of forfeiture. Additionally, it also includes particular stock appreciation rights (SARs), specific stock options and certain separation pay plans.
Example For IRS Section 409A
BLUESKY Inc. a fast-rising cloud storage startup known for its AI-powered data security solutions, decides to grant new stock options to its employees.
The company plans to grant stock options to its employees as part of a new incentive compensation plan at a board-determined value of $0.01. In the future, the IRS investigate this option price and evaluate the business.
| Founding Shares FMV (Board Determined) |
$0.00 |
| Options Granted | 50,000 |
| Options FMV (Board Determined) |
$0.01 |
| FMV (409A Valuation Determined) |
$0.05 |
| Difference | $0.04 |
| Price Difference (Difference * Options Granted) |
$2,000 |
| Tax Penalty | 20% |
| Penalty Amount (Tax Penalty * Value) |
$400 |
- The difference between the incorrect strike price ($0.01) and the current value ($0.05), is $0.04 per share for the 50,000 options received. This would give the total amount of $2,000, even if the employee has exercised the option or not.
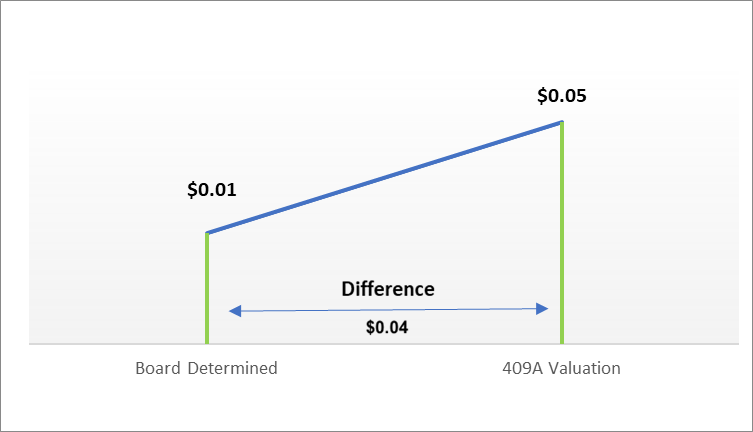
- Pay the penalty equal to 20% of the price difference. In this case, 20% of $2,000, which is a $400 penalty, must be paid to the IRS.
- Additionally, if the employee comes under the tax bracket of the 35% income tax rate, they would have to pay a $700 income tax.
So according to IRS Section 409A, the company would need to set the new stock options at $0.05.
IRS Section 409A Mandate
- Section 409A requires private companies like BLUESKY to obtain a 409A valuation to determine their common stock’s fair market value (FMV) before granting stock options or other equity-based compensation.
- This valuation ensures that employees don’t receive preferential tax treatment by purchasing stock at a price below its FMV.
409A Valuation Process
- BLUESKY engages an independent valuation firm with expertise in 409A valuations.
- The firm analyses BLUESKY’s financial data, business model, industry trends, and recent financing rounds.
- They apply valuation methods like discounted cash flow (DCF) and comparable company analysis to determine the FMV of BLUE SKY’s common stock.
- The firm issues a 409A valuation report stating the FMV per share.
Impact on Stock Option Grants
BLUESKY sets the exercise price of its stock options at $0.05 per share, equal to the FMV. This ensures compliance with Section 409A and prevents employees from receiving an unintended tax benefit.
Parts of the IRS Section 409A
| Definition of Deferred Compensation | Section 409A broadly defines deferred compensation as compensation that is earned in one tax year but paid in a subsequent tax year |
| Timing of Deferral Elections | This section outlines the rules for when deferral elections must be made, typically requiring that elections be made before the start of the tax year in which the compensation would otherwise be earned |
| Distribution Timing | Section 409A specifies when deferred compensation may be distributed, including upon separation from service, a fixed date or schedule, disability, death, a change in control, or unforeseeable emergency |
| Distribution Events and Restrictions | It sets forth the events that trigger the distribution of deferred compensation and any restrictions or penalties for early distributions |
| Penalties for Noncompliance | Section 409A imposes severe penalties on both the employer and the employee for noncompliance, including immediate taxation on the deferred amount, an additional 20% tax, and potential interest charges |
| Exceptions and Exemptions | Certain types of compensation are exempt from Section 409A, such as qualified retirement plans, certain stock options, and short-term deferrals |
| Documentary Compliance | Employers must ensure that their NQDC plans comply with the documentary requirements of Section 409A, including the timing of plan adoption and amendment procedures |
| Operational Compliance | Employers must also ensure that the operation of their NQDC plans complies with Section 409A, including the timing of deferral elections, distributions, and any amendments to the plan |
Even though we all aren’t lawyers, it’s good for business owners to have at least a basic understanding of the law for their company operations.
GENERAL SUMMARY OF SECTION 409A
A general summary of Section 409A is as follows: U.S. Code § 409A—inclusion in gross income of deferred compensation under nonqualified deferred compensation plans.
(A) RULES RELATING TO CONSTRUCTIVE RECEIPT
Below, we have listed the summary of rules relating to constructive reports:
1) Plan Failures: The rule imposes significant penalties for non-compliance. If a plan fails to meet 409A requirements, all deferred compensation becomes immediately taxable, and the recipient must pay a 20% penalty tax and interest on the underpaid taxes.
2) Distributions: Section 409A sets stringent rules regarding the timing of distributions from nonqualified deferred compensation plans. Distributions are permissible under specific conditions, such as separation from service, disability, death, a fixed schedule, or significant corporate events (like mergers or acquisitions).
4) Elections: The initial election to defer compensation must be made before the compensation is earned, typically by the end of the preceding year. Subsequent changes to the election are heavily restricted, generally requiring a minimum 12-month notice before changes take effect and significantly extending the deferral period.
(B) RULES RELATING TO FUNDING
Here’s a summary of the rules related to funding under Section 409A:
1) Offshore property in a trust: Under Section 409A, using offshore trusts or similar arrangements to fund nonqualified deferred compensation plans is prohibited. This rule is intended to prevent the transfer of assets out of the reach of U.S. tax authorities and creditors.
2) Employer’s financial health: Under Section 409A, using offshore trusts or similar arrangements to fund nonqualified deferred compensation plans is prohibited. This rule is intended to prevent the transfer of assets out of the reach of U.S. tax authorities and creditors
3) Treatment of Employer’s Defined Benefit Plan during Restricted Period: Assets set aside to fund nonqualified deferred compensation during certain restricted periods, such as when an employer’s defined benefit plan is underfunded, or the employer is in bankruptcy, are considered current income to the employee.
4) Income inclusion for offshore trusts and employer’s financial health: For assets located in offshore trusts or if assets are subject to financial health triggers, the compensation is included in the employee’s gross income in the year the assets are transferred offshore or the financial health trigger is implemented.
5) Interest on tax liability payable with respect to transferred property: For any deferred compensation subject to income inclusion due to violations of funding restrictions, the tax liability is increased by interest calculated at the underpayment rate plus an additional 1%. This interest accrues from when the compensation should have been included in income until actual inclusion.
(C) NO INFERENCE ON EARLIER INCOME INCLUSION OR REQUIREMENT OF LATER INCLUSION
Section 409A of the Internal Revenue Code states that compliance with its rules should not infer that deferred compensation must be included in gross income sooner or later under other tax code sections.
This means that just because deferred compensation is not included in your income under the rules of Section 409A, it doesn’t imply that the IRS cannot contain it under different circumstances or tax rules. Similarly, if compensation is included under Section 409A, it does not necessarily mean it must be included again under another provision.
(D) OTHER DEFINITIONS AND SPECIAL RULES
Section 409A of the Internal Revenue Code includes definitions and rules concerning nonqualified deferred compensation plans. Let’s look at the key terms and special rules:
1) Nonqualified deferred compensation plan: This term broadly covers any plan that defers compensation that is not specifically exempt, such as qualified employer plans or certain welfare benefits like sick and vacation leaves.
2) Qualified employer plan: These plans meet certain IRS qualifications and typically include tax-favored retirement plans such as 401(k)s and 403(b)s.
3) Plan includes arrangements: The term “plan” consists of any agreement or arrangement involving deferred compensation, even if it covers only one individual.
4) Substantial risk of forfeiture: Refers to the condition under which rights to deferred compensation are contingent upon future performance of substantial services or meeting certain conditions.
5) Treatment of Earnings: Earnings on deferred amounts are typically treated as additional deferred compensation, thus subject to the same rules and tax implications as the original deferred amount.
6) Aggregation rules: Similar deferral plans are treated as a single plan for compliance purposes, ensuring that all plans are equally compliant under the law.
7) Treatment of Qualified Stock: Employee stock options that meet certain criteria are not considered deferred compensation under Section 409A, provided they do not feature an additional deferral option beyond the inherent deferral of stock option gains.
(E) REGULATIONS
To implement Section 409A effectively, the Secretary of the Treasury will establish several necessary regulations:
1) Deferral Amounts Calculation: Establish guidelines for calculating the deferred amounts in nonqualified deferred compensation plans categorized as defined benefit plans.
2) Corporate Ownership and Control Changes: Set out rules regarding how changes in the ownership or control of a corporation or its assets should be handled, specifically under certain subsections of the law (a) (2) (A) (v).
3) Exemption Criteria for Arrangements: Define conditions under which certain arrangements (b) can be exempted from the rules of Section 409A to prevent improper deferral of taxes or assets being placed out of creditors’ reach.
4) Financial Health Definition: Provide a clear definition of what constitutes the financial health of a corporation as it pertains to the application of these deferred compensation rules (b) (2).
5) Risk of Forfeiture Guidelines: Offer flexibility in applying the substantial risk of forfeiture rule when necessary to fulfill the objectives of the section.
You can refer to the Cornell Law School for more details.
Why do you need 409a Valuation?
Now that you are clear about what IRS Section 409A is about, how do you know if you need a valuation or not? Well, the IRS usually requires companies that are planning to issue or that have issued option grants to get a 409A valuation done. This is important so that the company can calculate their price per share while maintaining a safe harbor status. Another reason is for startups and their founders to be aware of this rule so that the beneficiaries (shareholders) could avoid violating any of the rules and paying large penalty fees.
Therefore, it’s better to spend time to find a suitable 409A provider to help you with your company valuation. In fact, for you to get the safe harbor status, you will need to have the 409A valuation performed by an independent third-party company.
KEY POINTS ABOUT SECTION 409A IRS
Here are the key points about Section 409A of the Internal Revenue Code,
- Section 409A regulates nonqualified deferred compensation (NQDC) plans, commonly used to provide additional compensation to key executives. Failure to comply with Section 409A can result in significant penalties for the executive and the employer.
- The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) has acknowledged the complexity of Section 409A and, as a result, has established a program to help companies correct unintended operational errors under this section with lower penalties. This program, described in IRS Notice 2008-113, is a useful tool that offers guidance and assistance to ensure compliance.
- Companies must perform a 409A valuation at least once a year or whenever a significant change may impact the company’s value. This can include new financing, acquisitions, or changes to the financial outlook. The purpose of the 409A valuation is to determine the fair market value of the company’s stock, which is used to issue stock options or other equity compensation to its employees.
- An independent valuation specialist must perform the 409A valuation. The valuation report should include the amount, methods used, and specialist information.
- The IRS issued proposed 409A regulations in 2016, clarifying and expanding exemptions for Section 409A and guiding correction of noncompliant plan terms, especially for unvested deferred amounts.
What is 409a Safe Harbor? Types and Working
The safe harbor status of a 409A valuation means that you have some protection during an IRS audit. If you have a 409A valuation done for your company, the IRS would generally accept the stated company value unless they are able to prove that the valuation is “grossly unreasonable”. There are three kinds of safe harbor methods set by the IRS for getting the FMV of the private company’s common shares. These include:

- Binding Formula Presumption
- Illiquid Startup Presumption
- Independent Appraisal Assumption
Out of these safe harbor methods, the most common one is the Independent Appraisal Presumption. In fact, this method is used by 99% of private companies. By using this method, an independent appraiser uses the traditional methodologies and performs the 409A valuation for your company. The independent appraiser also needs to be a third-party and not someone who works in the company or is a close friend of the founders or board members.
How do you get a 409A Valuation?
Now that you know what a 409a valuation is and why you need it, let’s move on to understand how you can get one done. There are three options for how you can get a 409A valuation for your company. These include:
- Do it yourself. The first option is to perform the 409A valuation yourself for your company. The advantage of this is it saves you money rather than paying a business value to do it. However, it’s riskier as the valuation won’t have safe harbour status, and it’s more prone to mistakes. You also increase your risk of an IRS audit and possible penalties for your shareholders.
- Use software. This option is just like the one above, except the valuation is done using software to calculate the FMV of the company. However, it still has its own risk, as there is no safe harbour status for software generated valuations.
- Hire a firm. The last option is to hire a firm to perform the 409a valuation. As this option comes with a cost, it also offers you more protection as it has safe harbour status. This reduces the risk of an audit and the burden of proof is on the IRS. The valuer would also have more experience with assessing the value of your firm.
In short, choose the right option and hire a firm to get your IRS Section 409A valuation done properly.
What are the documents needed for the 409A valuation?
If you have selected an independent appraiser for your 409A valuation, you will need to begin collecting all the relevant information for the valuation firm. Although the list of documents will be similar for most valuation firms, a few things will be different.

To prepare for this, here is a list of the documents you need to gather:
#1 Company details
- Name of your CEO
- Updated Articles of Incorporation
- Name of your legal counsel
- Name of your external audit firm, if applicable
#2 Fundraising and options
- Your company presentation, executive summary, or business plan
- The number of options you expect to issue in the next twelve months
- The most probable timing of a future liquidity event
#3 Industry information
- Your industry
- Relevant public comparable companies. Many 409A valuations rely on some form of comparison to any publicly traded company when determining the FMV of a private company.
#4 Company financials
- Last 3 years of financial statements
- Non-convertible debt amount
- Cash burn and runway
- Forecasted EBITDA for the next 12 months (from the Valuation Date) & the next 2 calendar years
- Forecasted revenue for the next 12 months (from the Valuation Date) & the next 2 calendar years
#5 Additional details
- If there has been any material event that has taken place before the 409A valuation, or if any has taken place in the history of the company, you will have to share the details of this for your valuation.
What are the 409A valuation methods?
Once everything is in place, it is time for the valuation provider to start with the 409A valuation. There are three main 409A valuation methods used for getting the FMV of the shares of a company. Using one of these three methods, the valuation provider tries to offer the lowest strike price for your company’s shares. This is to reduce the tax burden on the shareholders when receiving the company’s equity.
In fact, there are many methods in the market used for 409A valuations, but these three are the most commonly used by business appraisers:
1. Market Approach
Out of all the three methods, this is the most common method used for larger corporations or those looking to raise new seed funding. This method takes similar public companies or data available from private companies, and compares their financial information to derive the company’s valuation.
2. Income Approach
In case the company has a good amount of revenue and a positive cash flow, that is when the income approach is used by the valuation provider.
3. Asset Approach
The asset approach is used mostly for the early stage companies that have not yet raised money and do not generate revenue. As per this approach, the total asset value of the company is determined to get the value of the company.
Find out more information on the 3 methods of company valuation here.
Penalties For Non-Compliance with Section 409a
Most 409a valuations that follow the common valuation methods would not be subject to penalties by the IRS. But if it doesn’t follow the rules as per IRS Section 409A, then the company may be subject to penalties. These penalties would be levied on the option holders, be it the employees, investors or shareholders.
Although many companies do not have to face an audit, the IRS still reviews company valuations to ensure enforcement of the law. If your company becomes successful and you are close to an exit (IPO or M&A), you may face an audit in the future. Hence, it is better to have a reputable firm helping you with this. Eqvista is one such firm that can help you.
FAQs
Below we listed Frequently asked questions for the IRS SECTION 409A,
What are the consequences of not complying with IRC section 409A?
Noncompliance with Section 409A can lead to substantial penalties, potentially resulting in significant tax obligations for employees, even if the violations were unintentional. It’s therefore essential for employers and employees to carefully structure and administer nonqualified deferred compensation plans.
What are the reporting requirements for employers under section 409A?
Reporting Amounts Includible in Gross Income under Section 409A, Reporting Nonemployee Compensation, and Interim Reporting Relief. Employers must carefully track and report amounts includible in income under Section 409A on employee W-2s and nonemployee 1099s while being mindful of the specific reporting requirements and deadlines.
What types of compensation are covered under section 409A?
Section 409A of the Internal Revenue Code covers a wide range of nonqualified deferred compensation arrangements, including Supplemental executive retirement plans (SERPs) and excess benefit plans, Salary and bonus deferral arrangements, Severance pay arrangements, and Taxable reimbursement arrangements.
How often should a company review its section 409a compliance?
The best practice is for companies to review their 409A compliance at least annually proactively and more frequently if material events could impact the company’s valuation. Maintaining proper documentation and working with qualified 409A experts can help ensure ongoing compliance.
What are the steps to take to comply with section 409A?
The key is proactively reviewing all deferred compensation arrangements, making necessary changes to bring them into compliance, and implementing procedures to avoid operational failures. Seeking expert guidance can help ensure that Section 409A requirements are properly addressed.
Top Tips for Staying Compliant with IRS Section 409A
- Work with an experienced, independent 409A valuation provider to ensure your stock option exercise prices are set at or above fair market value.
- Align your 409A valuation date with your month-end or year-end to make providing up-to-date financial statements easier.
- Design broad-based severance plans and window programs to comply with Section 409 A’s payment limitations.
- Ensure compliance with 409A for deferred compensation plans before the deadline.
- Get board/committee approval & modify deferred compensation plans by compliance deadline.
How can Eqvista’s 409a Valuation Help you?
Get your company’s valuation performed by Eqvista, one of the leading 409A valuations providers. Contact us to discuss your case today!
After reading this article, you now know that a 409A valuation is very important for your company, especially if you are giving out options or taking up new investments. And with all the information provided, you can now make an informed decision about your 409A provider. In fact, Eqvista offers 409A valuation services. We have an expert team ready to help you learn more about the value of your company.
Get in touch with our team and schedule a consultation with our valuation experts. We can discuss your company and how to go about getting a 409a valuation done in no time! You can also easily share the details of your company’s cap table on the Eqvista platform.
Interested in issuing & managing shares?
If you want to start issuing and managing shares, Try out our Eqvista App, it is free and all online!
