409A Valuations and Non-US Companies
In today’s interconnected economy, the lines between domestic and international business operations are blurred. One area that has gained attention is the intersection of global business practices and US tax regulations. As foreign companies seek to attract and retain top talent in the United States, they often navigate across unfamiliar legal terms.
Among the many compliance issues, “409A” has become increasingly relevant for non-US companies operating within or expanding into the American market. While initially designed for domestic corporations, these regulations have far-reaching implications beyond US borders. 409A valuations are important for non-US organizations that face extra challenges with cross-border tax laws and standards to ensure their equity compensation plans’ compliance with IRS regulations.
This article explores why non-US companies may need to comply with IRS Section 409A regulations, particularly when providing stock options or other equity-based compensation to employees in the United States. We’ll also highlight the implications of 409A valuations for global businesses operating in or expanding into the US market.

Scenarios Requiring 409A valuation for Non-US companies
Section 409A of the Internal Revenue Code sets forth specific rules regarding deferred compensation provided to employees, such as stock options. This regulation helps firms to accurately assess their stock’s fair market value (FMV) to prevent employees from incurring deferred taxes and penalties.
Equity Grants to US Employees
- Non-US companies must obtain a 409A valuation if they issue stock options or equity compensation to US citizens, residents, or taxpayers, even if the parent company is foreign.
- The valuation ensures the stock’s strike price meets IRS-determined FMV, avoiding penalties for employees.
US Subsidiaries or Market Expansion
- Foreign companies with US subsidiaries or those planning to expand into the US market must comply with 409A for equity issued through their US operations.
Cross-Border Mergers or Acquisitions
- Transactions involving US entities may require a 409A valuation to align with IRS standards and prevent post-deal tax complications.
Global Equity Incentive Programs
- Multinational companies often adopt 409A standards globally to simplify compliance, even if only a subset of employees are in the US
Compliance Requirements
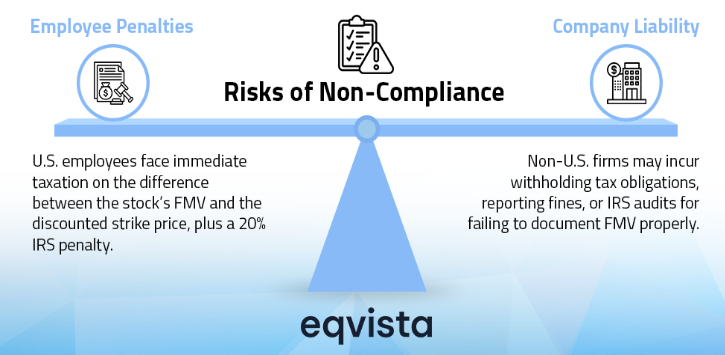
Non-US companies must comply with 409A regulations when providing equity compensation to employees in the US. Failure to do so might result in immediate taxation on deferred salary, interest, and extra employee taxes. A third-party valuation expert must conduct the assessment using US FMV standards, even if the company operates under non-US accounting practices.
A reliable 409A valuation for non-US companies gives potential hires confidence that their stock options undergo fair assessment, enhancing the company’s appeal as a workplace. Penalties for non-compliance with valuation can seriously affect employers and employees. Employees must immediately pay income tax on deferred compensation, along with a 20% additional tax and interest. A 409A valuation for non-US companies provides a comprehensive view of a company’s fair market value, which is valuable for financial and strategic planning purposes.
How Do Non-US Companies Calculate the Fair Market Value for 409A compliance?
Non-US companies calculate fair market value (FMV) for 409A compliance using methodologies similar to US firms but with critical adjustments for international accounting standards, market data availability, and IRS requirements.
Income Approach – Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Method
The DCF method calculates future cash flows of the firm and discounts them to present value using a risk-adjusted discount rate in order to estimate FMV. It is suitable for new firms and firms with high potential for growth. Interest rates, country risk premiums, and inflation adjustments are used in the computation.
Example: FMV Calculation in USD for a French SaaS Company
- The company generates US $550,000 gross per year during the primary period.
- The company incurs $ 330,000 in costs, leaving the following net operating income (EBITDA).
- EBITDA = Revenue – Costs = 5,500,000 – 3,300,000 = $2,200,000
- PV = Future Value / (1 + Discount Rate)^ Year
| Year 1 | Present Value = $2,200,000 / (1.14) = $1,929,825 |
| Year 2 | Present Value = $2,310,000 / (1.14)^2 = $1,777,470 |
| Year 3 | Present Value = $2,425,500 / (1.14)^3 = $1,637,143 |
| Year 4 | Present Value = $2,546,775 / (1.14)^4 = $1,507,895 |
| Year 5 | Present Value = $2,674,114 / (1.14)^5 = $1,388,851 |
We total these all to the overall present worth of $8,241,184 after five years from now. For the company to perpetuate constant growth with an assumed 5% after Year 5, we perform the following to determine value here:
Terminal Value = (Year 6 EBITDA) / (Discount Rate – Growth Rate)
Year 6 EBITDA = $2,674,114 × 1.05 = $2,807,819.
We therefore calculate: Terminal Value = $2,807,819 / (0.14 – 0.05) = $31,197,994
This terminal value would then be computed to its present value:
Present Value of Terminal Value = $31,197,994 / (1.14)^5 = $16,203,260
And overall market fair value (FMV) of the firm would be the addition of both calculated present value of its future earnings and present value of the terminal value:
Total FMV = $8,241,184 + $16,203,260 = $24,444,444
Market Approach – Comparison Company Analysis (CCA)
A company’s worth is determined using the market approach by evaluating other companies in the same market and comparing their stock prices or the value of the most recent mergers & acquisitions done in that area. Non-US firms adjust the valuation multiples for the other countries’ markets as per the existing conditions.
Example: Indian Manufacturing Company in US – FMV Calculation in USD
- The equivalent Indian firms’ industry EV/EBITDA average is 8x.
- The firm’s EBITDA is $700K.
With the average multiple of 8, the FMV would be $5.6M.
Asset Based Approach – Book Value Method
By deducting liabilities from both tangible and intangible assets, the Asset-Based Approach calculates the value of a business. It is best suited for highly asset-rich industries like manufacturing, real estate, and mining. Non-US companies adjust their financial statements using local GAAP or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
Example: A Singaporean Real Estate Company’s FMV Calculation in USD
The net asset value, or NAV (assets less liabilities), is $500,000,000 with $900,000,000 in total assets and $400,000,000 in liabilities.
What are the Differences Between 409A valuations for US and Non-US Companies?
It is essential for organizations operating internationally to grasp the differences in 409A valuation for non-US companies and US ones. This simple comparison highlights the main differences:
| Aspect | US Companies | Non-US Companies |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Framework | Directly subject to IRC Section 409A. | Must navigate both home country regulations and US IRC Section 409A requirements. |
| Valuation Frequency and Triggers | Annual or upon significant events like funding rounds. | Similar, but may also consider changes in exchange rates, international tax treaties, and home country regulations. |
| Valuation Methodology | Typically based on US GAAP financials. | May require adjustments to align IFRS or other financial standards with US GAAP for valuation purposes. |
| Tax Implications for Employees | Non-compliance leads to taxation, a 20% penalty, and interest on underpaid taxes. | Similar US tax consequences, but also must consider home country tax implications and compliance. |
| Operational and Compliance Considerations | Generally streamlined within the US legal and tax environment. | Requires additional efforts to align with US standards and may involve parallel equity plans or adjustments for global compliance. |
What are the Challenges of Obtaining 409A Valuation for Non-US Companies?
Getting a 409A valuation for non-US companies can pose distinct challenges for international firms, affecting their operations and compliance frameworks in various ways. Here’s a general overview:

- Compliance and Tax Implications of 409A Valuations for Non-US Companies -International organizations face the challenge of understanding US tax law and staying compliant with their home country’s tax regulations. Navigating both sets of regulations can be difficult, particularly when the laws do not match up. Failing to comply with 409A valuations can have significant tax implications, leading to severe penalties and taxes for the company and its employees.
- Equity Incentive Plans – Creating equity incentive programs that abide by Section 409A regulations can be challenging while still appealing and advantageous to US-based personnel. Non-US organizations must ensure their plans are compliant and competitive in the US market. It often involves updating or developing new plans considering US tax laws and the company’s overall compensation strategy.
- Limited Data of Non- US Companies – A lack of data for non-US firms makes it challenging to gather the necessary market information for a valuation, particularly for those in specialized industries or emerging markets. It can be difficult to determine a fair market value for equity compensation when there is limited access to relevant financial data about comparable firms.
- Language and Accounting Standards – Discrepancies in language and accounting standards can pose challenges for non-US during the valuation process. Financial statements and other relevant documents may require translation into English or conversion from International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) to US Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).
Best Practices For Non-Us Companies Seeking a 409A Valuation
Non-US organizations seeking a 409A valuation for their US operations can benefit from following best practices to ensure compliance and strategic alignment of their compensation plans. Here’s a simplified guide from basic principles and standard practices:

- Understand Valuation Requirements – Begin by understanding the basics of Section 409A of the US Internal Revenue Code. Understanding the factors that lead to a 409A valuation for non-US companies, such as granting stock options or deferred compensation plans to employees in the US, is essential.
- Legal Advice and Engage Qualified Professionals – It is advisable to consult with a legal professional and hire experts in the field. Seeking advice from legal advisors like Eqvista, valuation experts with expertise in cross-border taxation and valuations can offer valuable insights and guidance. These experts are skilled at dealing with the complexities of US tax law and ensuring that your valuation meets all regulatory requirements.
- Provide Accurate Financial Information – The quality of a 409A valuation for non-US companies depends heavily on the precision and thoroughness of the financial data supplied. Ensure your financial statements are current and accurately represent your company’s financial well-being. International financial reporting standards may need to be adjusted to align with US GAAP.
- Document Valuation Methodology – Clearly outline the methodology and assumptions applied during the valuation process. It promotes transparency and strengthens the valuation in case of inquiries from the IRS or other stakeholders.
- Consider Comparable Transactions –Use data from similar transactions in your industry to back up your valuation. It may involve recent funding rounds, mergers, acquisitions, or public market data. Nevertheless, locating pertinent comparables can be difficult, underscoring the significance of a knowledgeable valuation expert.
- Be Transparent with Stakeholders – Discuss the valuation process and its results transparently. This process involves staff, investors, and board members receiving equity compensation. Being open and honest fosters trust and allows for better expectation management.
- Stay Updated on Regulatory Changes – US tax laws and regulations may change, affecting valuation requirements. Keep your knowledge and practices current to stay compliant with the most recent rules and guidelines.
Get Accurate 409A Valuations From Eqvista!
Stepping into the US market opens up a world of opportunity, but it also comes with its set of challenges, especially around 409A valuation for non-US companies. At Eqvista, we’re here to simplify this process for you. Our expertise in valuations helps meet the unique challenges faced by companies like yours, providing clarity and confidence as you move forward.
Understanding 409A valuation for non-US companies can seem daunting, but with our support, it becomes manageable. We offer personalized guidance and valuation services tailored to your needs, ensuring your equity compensation plans are compliant and competitive in the US market. We believe in transparency and staying ahead of regulatory changes, so we continuously update our services to reflect the latest tax law and valuation best practices.
Have questions about how we can help your company with its 409A valuation needs? Contact us today.
