How can a Real Estate Business manage a 409A valuation?
Here is a summary of the 409a valuations for Real Estate companies performed by Eqvista.
Are you experiencing difficulties getting a fair market value of your real estate business? Real estate business valuation can be tricky and does demand various aspects to be covered. This article will provide information regarding the real estate valuation methods and different real estate valuation metrics that one can use while performing a business valuation.
Real Estate company 409a valuations by the numbers
Here is a summary of the 409a valuations for Real Estate companies performed by Eqvista. These average figures were obtained from the public markets, private markets, and our 409a valuations.
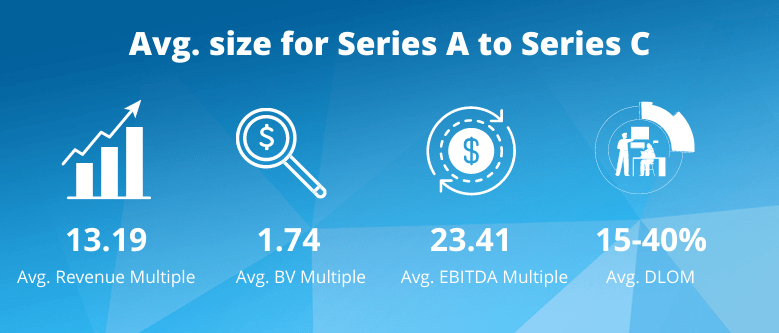
409A Valuation for Real Estate Business
The term ‘land’ is often used interchangeably with real estate, real property, but there are some definite distinctions between all these terms. Real estate is, but of course, the land added with permanent man-made additions such as houses and other buildings. The techniques used to analyze a real estate’s value are analogous to those used in the fundamental analysis of stocks. This is because the investment made in real estate is not a short-term trade. Therefore, analyzing the cash flow and the subsequent rate of return is essential in order to make profitable investments. Let us dive into the real estate industry and the need for real estate business 409A valuation.
Real Estate Industry
Real estate consists of the property, land, buildings, air rights above and subsurface rights below the land. As explained above, the term refers to real or physical property. As a business term, real estate also refers to manufacturing, buying, and selling property. It influences a country’s economy because it is one of the most critical drivers of economic growth.
Why Do Real Estate Businesses Need 409A Valuation?
Real estate business 409A valuation is required for several purposes, including the buying and selling property, appraisal of development, observing the property performance, tax matters, loan security, company accounts, and insurance reinstatement.
The lack of a central trading market means that investors in real estate cannot immediately obtain a valuation of their assets. Instead, the investors depend on independent valuers that offer the service. The valuation purpose and the property type to be valued will define the basis of the Valuation and the techniques one should employ.
Valuation Metrics to Consider in Real Estate Businesses
Given below are various real estate valuation metrics that one can use while performing business valuation:
Valuation of Real Estate Investments
The principal condition of the major investors is performance measurement, and valuations offer the data for this to be carried out. Data on capital value, Market Rent, and the components that have driven performance, such as yield shift and rental growth, provide the level of information needed to analyze the performance of real estate investments over different periods.
Cash Flow
As a landlord, you are in excellent shape if you can cover the mortgage principal, taxes, and insurance with the monthly rent. Just ensure that you have cash reserves in hand to cover that payment if you need to cover unexpected maintenance costs. A negative cash flow results from an investor having too much loan to buy the property. This can result in a default on the loan unless you can sell the property for a profit.
Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
Internal Rate of Return (IRR) calculates the interest you will earn on each dollar invested in a rental property during its holding period. Property’s potential rate of growth and the calculations goes beyond net operating income. Net Present Value (NPV) represents the value of money now versus in the future once the money has accumulated compound interest. The formula used is complicated, so many investors use the IRR function in Excel to estimate the ratio. A standard IRR metric ranges from 10-20% but can vary widely, depending on the particular real estate asset. It is a valuable way to assess whether or not a property is functioning well for you.
Net Operating Income (NOI)
Net Operating Income (NOI) guides how much money you get from a given investment property and is a version of a high-level income statement. To estimate this value, subtract operating expenses from your total income.
Operating expenses consist of property manager fees, legal fees, general maintenance, property taxes, and any utilities that you pay. It includes everything from extra parking, laundry machines, or any service fees in your total income. It is advised to never include mortgage payments in the NOI calculation as they are not operating expenses. Investors solely use NOI to judge a building’s ability to generate revenue. It defines a specific investment that will generate enough income to make mortgage payments.
Loan to Value (LTV) Ratio
Loan to Value (LTV) Ratio helps measure the amount of leverage on a specific asset. LTV is valuable to buyers who finance their deals as it determines the amount needed to finance against the property’s fair market value. It is the best way to track the equity you hold in a property for the value of your portfolio and assets accounting.
The following example can define the importance of LTV: If the lender does 80% LTV deals, you will require a 20% down payment to secure the mortgage. In this scenario, a $100,000 property would need $20,000 as a down payment plus closing costs, representing an 80% LTV. After 10 years, if the property’s value is now $200,000 and you’ve paid down your mortgage to $50,000, your LTV would now be 25%.
Price to Income Ratio
The price to income ratio differentiates the area’s median household price from the median household income. In 1988, it was 3.2. After the housing bubble in 2011, it increased to 3.3, and in October 2020, it was raised to 4.0. Before the housing bubble crashed, it was defined at the peak of 4.66.
Price to Rent Ratio
The price-to-rent ratio is used to compare median home prices and median rents of a specific market. To calculate the cost to rent ratio, all you need to do is divide the median house price by the median annual rent to generate a ratio. As a general rule of thumb, customers must think of buying when the ratio is under 15 and rent when it exceeds 20. Usually, markets with a high price/rent ratio do not offer a good investment opportunity.
Gross Rental Yield
For a property, one can find the gross rental yield by simply dividing the annual rent collected by the total cost of the total property and then multiplying that number by 100 in order to get the percentage. The cost of the total property consists of the purchase price, all closing costs, and renovation costs.
How Valuation is done or Real Estate Business
One can consider several elements for value determination, the most effective is the Income and Market method. The three main methods that are used are:
- Market approach – The market-based approach utilizes financial information from publicly traded companies from the same industry and operations, including revenue, net income, EBITDA, etc. These are then used to contrast with for estimating the company’s equity value with a valuation multiple.
- Income approach – The Income Approach is a very straightforward approach used for companies with a positive cash flow and sufficient revenue. The company’s future forecast of cash flow is then discounted to find the company’s net present value (NPV).
- Asset approach – The asset approach is the least supported 409A business valuation approach. It is essential for very early-stage firms that have not raised any funding and do not have any revenue yet. This method takes the current book value and finds the company’s value from its balance sheet.
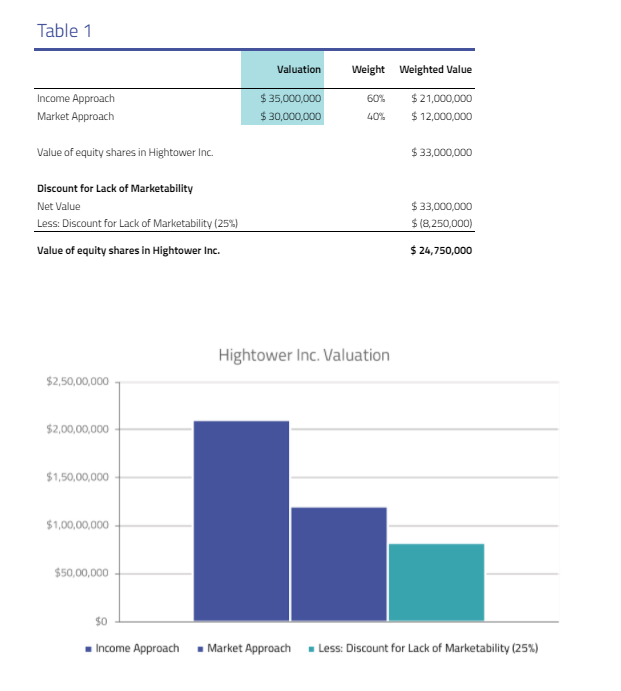
Here is a sample of our 409A valuation report of an example real estate company:
Choose Eqvista for Real Estate Business 409A Valuation
Real estate valuation is conducted based on strategies that are almost the same as that of equity analysis. Several other methods adding up to NOI, Gross income multipliers are also used frequently. Real estate agents help people, businesses, and investors by guiding them in buying and selling properties.
Many industry experts define the fastest appreciation rate as a result of development patterns. Irrespective of the method used, the most important predictor of the success of any strategy used is how well it is researched. Eqvista can help you with your real estate 409A valuation. It offers many other services that might come in handy when it comes to running a successful business. Contact us to learn more!
Interested in issuing & managing shares?
If you want to start issuing and managing shares, Try out our Eqvista App, it is free and all online!
