409A Valuation – Guide for Founders
A 409A valuation is a third-party, independent appraisal of the fair market value of a private company’s common shares.
Many businesses use equity as a tool to raise funds and offer to employees, but it is not as simple as it may appear. When looking for investors, a startup’s valuation is done to evaluate its relative worth so that an investor can figure out what percentage of the company they should get in return. These assessments are significant, but they do not reflect the underlying value of a startup at the time of the transaction.
This article serves as a guide for founders on 409A valuations. It explains what these valuations are, why they are important, and how to obtain them. Our insights will help founders understand 409A valuations, enable founders to make informed decisions and ensure compliance when issuing equity to employees.
What is a 409A valuation? Why is it important for your business?
A 409A valuation is the assessment that determines the FMV of your company’s common stock, establishing the minimum price at which you can issue stock options. This is critical for your business because it ensures compliance with IRS regulations when offering equity compensation, helps avoid tax penalties, and provides defensible documentation in case of an audit. The approach used should align with your company’s current financial stage.
With a proper 409A valuation, you can confidently issue options, attract talent, and maintain compliance while demonstrating proper governance to investors and stakeholders. Proper 409A valuations start with understanding your company’s current financial stage.
Understanding the 409A Landscape
The market size for the 409A Valuations Providers Service Market was valued at around USD 2,585.29 million in 2024. It is expected to reach USD 5,663.8 million by 2032, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.3% during the forecast period of 2025-2032.
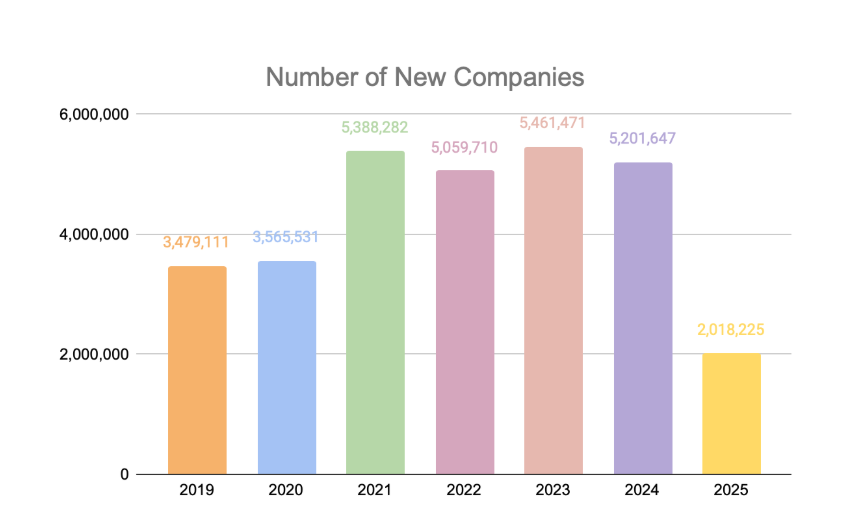
Number of New Companies Over the Years
From 2019 to 2025, the number of startups incorporated in the United States experienced ups and downs based on a number of factors including the COVID-19 pandemic.
In 2019, approximately 3.4 million new business applications were filed. This number increased in 2020, reaching about 3.5 million.
The upward trend continued in 2021 with approximately 5.4 million new business applications, marking a 19% rise from 2020.
Despite a slight dip in 2022 to around 5.0 million applications, the numbers bounced back in 2023 with a record high of approximately 5.5 million new business applications.
In 2024, the United States saw a slight decrease in new business applications to about 5.2 million for the year.
Through April 2025, approximately 2 million new business filings have been submitted, showing continued robust interest in starting a business.
| 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 (till April) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of New Companies | 3,479,111 | 3,565,531 | 5,388,282 | 5,059,710 | 5,461,471 | 5,201,647 | 2,018,225 |
409A Valuation Report
A 409A valuation report is a formal document that establishes the fair market value (FMV) of a private company’s common stock. This valuation is primarily used to set the exercise price for employee stock options and other equity compensation.
IRS does not provide any precise instructions as to what should be included in a startup 409A valuation report. However, there are a few key aspects that must be included in the report, such as the valuation, the methodologies utilized, and everything about the company that contributed to the firm’s value determination. It also considers the bigger picture of the environment and economy in which the firm operates to get a more accurate image of how much the company should be worth right now.
Key aspects of a 409A valuation report
- Purpose – It helps companies comply with Section 409A of the IRC, which requires that stock options be granted at or above fair market value to avoid tax penalties.
- Contents – The report typically includes company financial information, industry analysis, valuation methodologies used, and the resulting share price determination.
- Methodologies – Common approaches include the market approach (comparing to similar companies), the income approach (discounted cash flow analysis), and the asset approach (evaluating the company’s tangible and intangible assets).
- Timing – Companies typically get a new 409A valuation every 12 months or sooner if any significant changes occur (like significant funding or major business changes).
- Consequences – If options are granted below FMV without a valid 409A valuation, employees could face severe tax penalties, including immediate taxation and an additional 20% federal tax.
How Does a 409A Valuation Differ by Funding Type?
A 409A valuation differs by funding stage or type in the following ways:
409A Valuation for Seed/Pre-Seed Stage
- Seed-stage companies typically have a lower 409A valuation, often in the $1-10 million range.
- Limited financial data and operational history are available to analyze, so the valuation relies more heavily on market comparables and qualitative factors.
- The 409A valuation has a 12-month safe harbor period to grant options at the same strike price.
409A Valuation for Series A
- Series A companies tend to have a 409A valuation of $10-30 million.
- More financial data is available, including revenue projections, allowing for better cash flow analysis.
- The valuation considers the company’s ability to execute its business plan and generate future profits.
409A Valuation for Series B
- Series B companies’ normal 409A valuation range is $30-60 million.
- Valuations focus on the company’s potential to become a market leader and its strategic plan to drive revenue growth.
- Auditors and legal counsel are typically involved in determining an appropriate valuation cadence, often annually.
409A Valuation for Series C and Beyond
- 409A valuations are typically $100-120 million or higher for late-stage companies.
- The company’s ability to execute its strategy, achieve market leadership, and generate substantial revenue is stressed.
- Valuations may be conducted quarterly in preparation for an IPO within 12-18 months.
Example of 409A Valuation Report for Funded Companies
Most companies we encounter who need a 409A valuation do it for option pricing (setting the exercise price of their options, most likely ESOPs, after fundraising). For this, they need to comply with setting a correct exercise price.
With most VC-backed companies, their funding serves as a basis for the valuation method, ie. Backsolve and the 409A valuation also take on the pre-money valuation as taken through the round.
Let’s take an example to see what the 409A valuation would look like. Let’s say there’s a company called BioStart Inc., which just received a Series A funding round of $5 million dollars for $2.00 as share, off a pre-money valuation of $18 million.
This is a snapshot of their Cap Table and how the valuation was arrived at:

If we do some simple math, we can take the $5,200,000 capital committed by the Series A investors and divide it by their ownership percentage of 28.69% (excluding any rights).
Simply put, $5,200,000 / 28.69% = $18,124,782 or around $18 million at post money, or $12,924,782.15 pre money valuation. We can take this as a base for when doing the 409A valuation.
For Biostart Inc., we can see that the company has five different securities: Series A Preferred Stock, Seed Preferred Stock, Common Stock, Options @ $0.25, and their ESOP (Employee stock option plan) at 10% of the total shareholdings. The details of this will be crucial for the backsolve method later on. This method considers two main methods, a waterfall analysis and stock options pricing model, and calculates the value from the bottom-up on who receives value first and how much each receives.
With the information that BioStart Inc. predicts a probably exit within 4 years, here is how the breakdown would look like for each amount for a waterfall analysis:

- Breakpoint 1: At the first breakpoint, the Series A and Seed Preferred Stock shares a percentage of the total $6,450,000 invested in the company at 80.6% to 19.4%.
- Breakpoint 2: In the second breakpoint, the common stock would receive 100% of the value before any value goes to the option holders.
- Breakpoint 3: In the third breakpoint, the $0.25 strike price options get the value of the company and share with the common stockholders at 12.20% to 87.80%.
- Breakpoint 4: In the fourth breakpoint, the anticipated ESOP gets value and shares with the other option holders and common stock at a split of 73.24%, 10.17%, and 16.59%.
- Breakpoint 5: In the fifth breakpoint, the Seed Preferred Stock converted to common shares, as they would be gaining value per share over their $1.25.
- Breakpoint 6: In the fifth breakpoint, the Series A stock converted to common shares, as they would have a value of over $2.00 per share. This is the last tranche, so all equity classes would split the value according to their cap table ownership.
After running the calculations using the backsolve method, which involves using the Black Scholes Stock Option Pricing models, we calculate the hypothetical value of each Breakpoint to arrive at the $2.00 per share of the recent Series A funding.

From the backsolve, we find that the company is valued at $14,434,106, which is close to our ballpark figure.
We can use this same method for finding the common share price (which becomes the option strike price) using the same calculations:

With the backsolve method, the common strike price (Pre-DLOM) is $1.42 according to the cap table structure.
As the company is still running at a loss and has other risks, a DLOM of 50% was applied to the common share price as:
$1.42 Common Share Price x 50% DLOM = $0.71 share price
This $0.71 would be set as the exercise price of the ESOP to be issued.
This price also represents around 35% of the $2.00 round ($2.00 / $0.71).
Some interesting myths and facts about 409A valuation
Despite the fact that the 409A valuation structure has become well-established, several early-day fallacies have survived. The four most popular are debunked in this section.
Maintain the lowest strike price at any cost
You cannot specify an option strike price that is lower than the computed FMV, but you can set one that is greater. Regulatory and tax authorities are often only concerned when the strike price is set lower than the 409A valuation supported.
409A valuation creates a tax burden
Suppose the IRS gets involved and determines that your 409A valuation doesn’t fall under the safe harbor. In that case, all of the stock you granted to your employees under that FMV becomes part of their gross income (including interest owed) all at once in that year (not just the current taxable year, but any prior year). On stock options that vested prior to that tax year, the IRS might charge a penalty of up to 20%.
Have a negative influence on M&A and IPO
The buyer will look over your 409A valuations during M&A due diligence. In general, bad 409A procedures come across as sloppy, and they won’t help you set the tone for talks. If the buyer is unhappy, they can change the terms of the transaction so that they are not responsible for any financial burden associated with the mispriced options; they can demand that you indemnify them for the risk, or they can demand that you pay (or force your employees to pay) any associated penalties and taxes related to the affected option grants.
How to get a 409A valuation?
A 409A valuation is a third-party, independent appraisal of the fair market value of a private company’s common shares. The assessment conclusions are reported to the company’s board of directors in the form of a 409A valuation report, which is used to decide and set the price at which people can buy shares of the company’s common stock.
Requirements for getting 409A valuation
The valuation must be conducted by an independent third party with expertise in assessing private company valuations. This ensures compliance with IRS regulations and establishes “safe harbor” status.The company must have information like Past financial data, Projections for the next 12 months, information about preferred equity or convertible debt sales if applicable, and in certain cases, Key performance indicators, customer contracts, and strategic partnerships may be considered.
What does it cost to get a 409A valuation?
The cost of a 409A valuation will vary depending on the stage, complexity and provider.
Cost range:
- Early-stage startups – $2,000 to $5,000 for companies with simple financial structures and minimal historical data.
- Mid-Stage Companies – $5,000 to $10,000 for businesses with moderate complexity, such as multiple funding rounds or diverse ownership structures.
- Late-Stage or Complex Companies – $10,000 to $25,000 for companies nearing an IPO or with intricate share structures and significant financial history
Eqvista provides 409A valuations at a price 30% lower than other providers while maintaining the high quality of the valuation report.
Penalties for Noncompliance with 409A Rules
Employees must pay income tax and a 20% penalty on any deferred vested amounts under the NQDC plan as of the last day of the vesting year, even if payment happens in later years. If your NQDC arrangements are subject to 409A requirements and you have an operational failure, the IRS can tax and penalize all of your NQDC arrangements.
Employers face penalties for failing to withhold taxes correctly on deferred compensation. Noncompliance could lead to employee lawsuits and damage the company’s reputation if employees face unexpected tax liabilities.
Choose the right 409A valuation service provider
The IRS says a firm should have extensive experience of relevant company valuation experience. One must look at these parameters to determine the valuation service provider:
- Look for the reputation and 409A valuation reviews – There are several methods for assessing a company’s reputation. They include media analysis, stakeholder surveys (customers, employees, investors, NGOs), focus groups, and public opinion polls, among others. You must be aware of the market reputation of the 409A valuation service provider, how many clients they have, the client experience, and the conversion rate.
- Check how much they charge – It is important to know the price of the valuation provider. It must be cost-effective as well as be able to provide quality and accurate reports. One can differentiate pricing by looking at the features, add-on services, and customer support.
- Comply with IRS guidelines – The IRS is in charge of enforcing the federal tax laws that Congress passes. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) is in charge of enforcing federal tax laws enacted by Congress. Tax return processing, taxpayer assistance, and enforcement are the three core duties of the IRS.
- 409A valuation preparation time – In most cases takes less than a month to prepare. Unless you have a pressing need, most firms will complete one in a fair amount of time.
Tips From Our Experts
The right approach depends on your business reality, not preference.
Be clear about the Company’s current financial situation, which defines the valuation approach.
- Pre-revenue? Then mostly likely asset-based (unless you expect high sales in the coming 12 months).
- Recently funded? Then backsolve is probably the best fit.
- Revenue generating, but no identifiable forecast? Then the valuation would be through a market approach. If an old business with steady revenue and profit, probably a mix of market & income based.
We’ve had many clients coming in wanting this approach or that approach when it doesn’t really fit. This not only makes the valuation and FMV hard to determine but also offers weak support in case of an audit.
For similar company comparables, it’s useful to provide the most relevant companies in the public market for reference, even if the Company is unique.
We understand the main purpose of a new startup is to be unique, with a different offering than what the market has. But for valuation purposes, we still need to compare the company with other existing companies. So mentioning that there are no other similar comparables, doesn’t help with our analysis.
For recently funded companies, provide the detailed cap table and information of the round.
Countless times we have done 409a valuation cases for recently funded companies, and their cap table is messy and lacking a lot of information. It takes days to chase after information on share rights, liquidation preferences, stock option strike prices, and others, for the client to come back asking why it’s taking so long.
If we have a full view of the information, the analysis can be quite quick. Or at least we can generate a base range on the FMV before releasing the report.
The Strike Price is the lowest FMV you can issue options, but you can always issue higher
Some companies, after requesting their 409a, think the result is too low (feel it would affect their shareholder confidence), and request a change to increase this. Then later come back and want a lower valuation for their 83b filings or personal tax purposes.
If issuing an ESOP plan, you can issue an FMV above your 409a price. For example, if the 409a valuation comes in at $0.05, you can issue new stock options at $0.10 if you main concern is showing value to your shareholders.
FAQs of Founders on 409A Valuations
For most companies, a 409A valuation can be a complicated process to understand. Many founders are aware of the importance of a 409A valuation, but they may not necessarily know all of the important details. We have helped answer some of the frequently asked questions from founders to help you understand more.
Why 409A Valuation Important?
- Required by the IRS to set the strike price for stock options and other equity compensation issued to employees and service providers
- It helps startups comply with IRS regulations and avoid potential penalties for undervaluing or overvaluing stock.
- Assures employees and investors about the accurate valuation of the company’s equity
When to Get a 409A Valuation?
- Startups must get an initial 409A valuation before issuing stock options or other equity compensation/li>
- A new 409A valuation is required at least once every 12 months.
- Additional valuations may be needed after material events that significantly impact the company’s value, such as fundraising rounds, acquisitions, or changes in business model.
How to Choose a Valuation Provider?
- Founders should select a reputable valuation firm with experience working with startups and conducting 409A valuations.
- Consider factors like expertise, reputation, cost, and turnaround time when choosing a provider.
What is the difference between market value and fair market value?
A fair market value is the fundamental value of equity, based on present conditions that are considered to be free from any kind of market forces. While the market value is the estimation of the value of the equity if it was available to the public.
In fact, the market value has more to do with supply and demand in the market, and in comparison, 409A valuation determines the fair market value that is based on the financial projections, cash flows and tangible and intangible assets of the company.
How secondary trading can impact 409A valuation?
There is a significant probability that the 409A valuation is impacted by secondary trading. The factors that can impact 409A valuation include seller and buyer motivation, the similarity of securities that are sold, the volume of the transaction, information asymmetry, proximity of timing, or deal structure.
Hence, startups should know about the impact of secondary trading on 409A valuation and should be able to take appropriate measures. Eqvista’s team of experts is always available to guide startups through the entire process.
Why choose Eqvista as your expert valuation firm for 409A valuation?
By understanding the importance of 409A valuations and following the proper procedures, startup founders can ensure compliance with IRS regulations and maintain the integrity of their equity compensation plans.
By choosing Eqvista, companies can benefit from their expertise, efficient processes, and commitment to delivering accurate and defensible 409A valuations that comply with IRS regulations. Eqvista’s experience with startups and private companies makes them a suitable choice for businesses seeking reliable services. Beyond this, Eqvista provides complementary services like cap table management, incorporation assistance, and scenario modeling, offering a comprehensive solution for startups.
Interested in issuing & managing shares?
If you want to start issuing and managing shares, Try out our Eqvista App, it is free and all online!
