SaaS Valuation: How do you value a SaaS company?
Valuing a SaaS company can be a complicated process if you are not well-versed with all the terms and factors that assists in doing so.
SaaS is Software as a Service. With an expanding market for software, many businesses offer services worldwide through a web-based application using the SaaS business model. Software as a Service reshaped the way companies satisfied their customer needs making it more efficient in every aspect.
What is a SaaS company?
A SaaS company is an organization that utilizes software to host an application where their customers can access their services. The company creates and develops a service that they provide to their customers on a web-based platform. Customers can access these services remotely without any restrictions globally. This service can expand globally without raising the cost of delivery.
SaaS Business Model and Examples
In a SaaS company, servers that contain the database are maintained along with the software that permits the application to be accessed. Customers can reach the software application on the web through browsers from any device. Customers of a SaaS application usually have to subscribe and pay a fee either monthly or annually. Generally, a user’s subscription depends on the amount of data they need to store. Different types of subscriptions are available based on various factors like the number of users, the level of technical assistance required, or the total amount of data space needed.
There is a business function for every line in an organization. The most popular SaaS applications are:
- CRM or Customer resource management. Companies provide this application to businesses so they can manage their customer data and track their sales through each pipeline. For example, Salesforce is a company that provides B2B CRM assistance to all types of organizations.
- Project Management is a software that company provides to other businesses. This software assists the associates in communicating and staying on course. For example, Teamwork Projects is a B2B company that provides project management to other companies.
- Some companies focus on providing accounting and invoicing services to other businesses. The offers range from reporting services to financial tracking. For example, Zoho Books provides accounting and invoicing services to other organizations.
- Data Management is another type of service that companies offer. They help to analyze and secure the company’s data on the cloud.
- Web hosting and e-commerce on remote servers handle all aspects of an online business. An example of a web hosting software is Bluehost.
- Human Resource software offers businesses to manage and schedule the hiring process, manage the payroll, and track employee hours. One such company that provides such software is BambooHR.
- ERP or enterprise resource management is a system that consists of and offers various SaaS applications to big companies.
Benefits and Risks
When looking at the benefits of SaaS, multi-distribution is one main factor that helps standardize many applications such as email, customer service, relationship management, web conferencing, and enterprise content management. Other benefits include:
- Low Cost
- Convenient with on-demand service
- No installation of custom software is required
- More elasticity, allowing the customers to expand their use of this service without facing huge expansion and hardware costs
- Much better processing, storage, and collection of data in huge quantities
- Professional data management services are available
- Can be accessed from different locations
- Low risk of failure and loss of data
This service has not been fully developed yet and has some drawbacks. Due to the lack of development and still prematurely growing market there are some risks associated with it such as:
- Bottleneck data, and other limitations over the internet
- Service discrepancies and network dependence
- Lack of control with the customer
- Breaches of data and loss of data
- Sometimes fails to backup data
- Reserved rights to edit or delete the application programming interface
- It has a fixed and non-negotiable pricing structure
- The SaaS provider monitors and collects the customer data for commercial use.
Valuing a SaaS Company
Valuing a SaaS company can be a complicated process if you are not well-versed with all the terms and factors that assists in doing so. The following points will help with valuing a SaaS company.
#1 Understanding SDE or Seller Discretionary Earnings
The Seller Discretionary Earnings is the Revenue – COGS – OPex + Owner compensation.

Let us first understand these terms:
- Revenue is the sales that the business operations generate.
- COGS refers to the direct cost the company incurred for producing the goods sold.
- OPEX is the main operating expenditures of the business, such as rent, utilities, and salaries.
- The wages paid to the owner for his work is the owner’s compensation.
The SDE (Seller Discretionary Earnings) generally values businesses that are valued under $5 million with no management team and have a slow growth rate. Using SDE is the best way you can reflect the underlying earnings and power of a small enterprise accurately. A majority of the small and medium enterprises rely on the owner, and it is common to have expenses and wages associated with them. The wages the owner pays themselves might not be the same as the market rate. The owner can also record personal expenses under the company’s name to avoid tax. All these expenses are added into the calculation to determine the true and full potential of the earning power.
#2 Understanding EBITDA
EBITDA is the earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization. It is a financial metric that is widely used to measure the overall financial performance of a business. EBITDA shows how profitable a company is. EBITDA is not the only metric you will need to determine the performance of your business, but you will also need the revenue of the business as it will provide insights about the incoming profits and money that the company has. To see where you stand, you will have to calculate the EBITDA margin and compare it to the average of the industry.


For example, Company XYZ has an EBITDA of $100,000.
- Total revenue = $1 million.
- The margin of EBITDA is 10%.
Company ABC has an EBITDA of $120,000.
- Total revenue = $1.8 million.
- The margin of EBITDA is 6.667%.
Company ABC has a higher EBITDA (120,000) when compared to Company XYZ (100,000). But the margin of EBITDA is smaller than XYZ (6.667% to 10%). When viewed from an investor’s perspective, company XYZ is more favorable.
#3 Revenue
The major factor that differentiates SaaS companies from traditional companies is that they have to invest a considerable amount upfront to boost their growth. When determining the EBITDA, these amounts that were invested will be considered as expenses.
Here is where revenue becomes more essential. Since the upfront investments are deemed as expenses in growing companies, it becomes essential to measure the revenue. In case the company does not have any revenue, there will be no data to support the forecast, and you will not be able to accurately determine if it will be profitable to purchase the business. With fewer data available, the amount determined can be overvalued.
Key Variables
While valuing SaaS companies, there are some key variables to keep in mind as they play an essential role in the calculation.
- The company’s Qualified Marketing Traffic
- Customer Engagement Score
- Average amount billed per customer
- Lead-to-Customer rate
- Leads by Lifecycle Stage
- Customers Health Score
- Revenue Churn
- Customer Churn
- Total number of accounts
- MRR
- CAC:LTV Ratio
- Customer Acquisition Cost
- Months to Recover CAC
- ARPA
- Cost Of Goods
- Number of Customers
- CLTV
- Customer Lifetime Value
SaaS Valuation Multiples
SaaS valuation multiples are the financial tools that will help valuate one financial metric as a ratio of another metric. Multiples help make different companies comparable. It consists of various factors, but what matters more is the transferability, sustainability, and scalability of the business. Here is how to find the SaaS valuation multiples.
Finding the Multiple
For SaaS companies, the multiple a company gets is dependent on several factors. SDE multiples of such companies range from 3x to 5x. Here are a few important factors that helps to find the multiple:
- Involvement of the Owner: Usually an owner runs a majority of small businesses. Potential investors find businesses that can run without the owner more appealing. Businesses with a strong team that run the company without the owner often receive a premium valuation multiple when compared to those that operate under the owner.
- The SaaS company’s age: If the company has been running for a couple of years and has a track record with sustainable earnings, it will be easy to evaluate the forecast. If the company has been running for 2 years, the valuation multiple will be higher than a startup. If it has been running for more than three years, investors will present a higher multiple. This does not mean that young startups do not attract investors. Young startups will attract more high-risk investors with high tolerance.
- Growth Rate: Investors find it appealing if your company has a sustainable and predictable growth rate. A company that has more predicted and stable growth rate is more attractive than a business with distorted and unpredictable growth rates.
- Market Trends: No owner will want to sell their company that is growing rapidly in a trending market. Also, no investor will want to buy a company that is in a declining market. The ideal place for a company to be is in a more consistent trending market along with sustainable growth.
- Customer Metrics: One of the most essential metrics in the SaaS valuation is the consumer metrics. Investors have a close eye on these metrics; one of the metrics is Churn. Churn is a common metric in SaaS companies that offer services on subscription.
Important Metrics to Consider While Valuing a SaaS Company
While valuing SaaS companies, you must consider the essential metrics. This will make sure that your valuation is as accurate as possible.
#1 Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) and Customer Lifetime Value (LTV)
The CAC (Customer Acquisition Cost) is the total sales and marketing costs incurred to attain one additional consumer. The less your company spends to get an additional customer, the better. There cannot be an average that applies to all companies since it is different for every company. To make a close comparison to your company, you will also need to determine another metric, the LTV (Customer Lifetime Value). The average amount that a company earns throughout the time a customer pays for the service they subscribe to is the LTV. The higher the amount, the more precious each customer is to the company. Similar to the CAC, the LTV has no average amount that all companies can use.

The amount will differ depending on factors such as the competition, market, business model, etc. The LTV/CAC ratio is required in valuing SaaS companies. These two numbers will be compared to each other to determine a ratio that shows if the company is making more than they are spending to acquire a customer. The ratio will also permit us to determine the ROI of the marketing and if the strategies for growth are actually working. Generally, the ideal LTV/CAC ratio is 3 for a majority of SaaS companies. This allows a cushion zone to account for any increase in the CAC or dip in the LTV, and the company will still be able to generate stable gross profit.

#2 Churn Rate
Usually recorded in percentage, the churn rate is the number of customers who stopped using your services by unsubscribing within a specific time period. One of the most important SaaS growth metrics is the churn rate, as it tells investors if the company will be able to sustain growth. A high Churn rate indicates that the company is not suitable for the SaaS recurring business model. The ideal rate for a company is below 10%, if the business has a churn rate below 5%, it will put your company in potential investors’ sweet spot.
#3 Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) vs Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR)
Owners are often tempted to sell their annual plans at a reduced price to improve the company cash flow in small or medium self-funded SaaS companies. While this may be necessary in many cases, it holds the company back from the valuation perspective. The SaaS metric of revenue for SaaS growth metrics and to value an investor is::
Monthly recurring – Annual Recurring – Lifetime
This is usually the exact opposite of what the owner would want to do, especially when they want more capital growth. Even if the growth is slow, by selling monthly plans, you eventually achieve higher valuations. The MRR often outweighs the advantages of short-term cash flow boost as data shows that it is generally valued around two times more when compared to lifetime plans of equivalent revenue.
An average SaaS company has an MRR to ARR ratio of 5:1. To maximize the SaaS valuation of the company, this is the ideal ratio. Let us take an example, a company has 10 customers that are paying $200 per month and 5 customers that are paying $100 per month. This makes the MRR $2,500. If 2 customers have subscribed to a yearly renewal agreement for $250 then the ARR will be $500.
These products are generally annually priced at 10-20% lower than the monthly plans. SaaS products that have a higher ratio of annual plans will see a lower valuation. This is because the revenue is not only less predictable but also unstable.
Evaluating SaaS company metrics throughout company lifecycle
As a SaaS company grows, there are different key metrics that you need to know as it helps to understand organizational health. Additionally, it also helps to determine the best way you can optimize your business. Throughout the company lifecycle, the process to determine each metric and its importance keeps changing. Here are the various stages and the key metrics important in them:
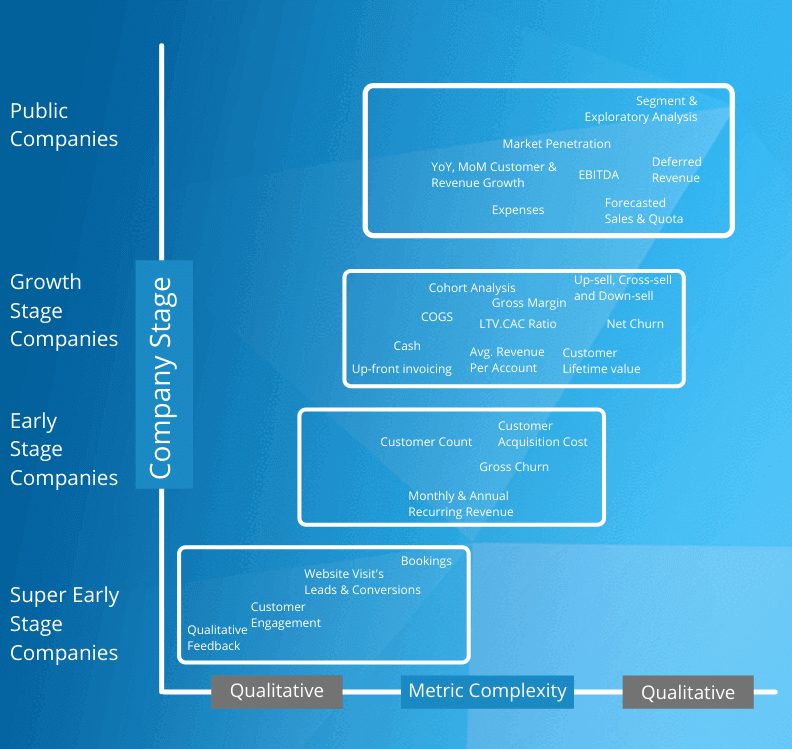
- Super early stage – Businesses that are in their super early stage look for product fit and have less detailed financials. As they move on from early-stage funding to Series A the metrics necessary are the MRR and/or ARR, the CAC and the marketing and sales cost.
- Early stage – When the company gains traction and starts to move, they look for expansion and growth through the Series C and D rounds of funding. The management is now more focused on the efficiency of the company. The key metrics in this stage are: the ratio of CLTV and revenue, gross margin, Churn rates, and ARR.
- Growth stage and Public Companies – In this stage of the life cycle of a company, there are many magical moments such as an IPO. New metrics are on the top of the priority list as the management is not looking at the future to gain more visibility. They look at the overall expenses, deferred revenues, their EBITDA, growth in the number of customers over the years.
How to sell your SaaS Business
If you have decided to sell your SaaS business, you should consider all the options you have to make an exit. Generally, when an owner of a SaaS business wants to make an exit, they have four avenues. It is important that you consider each avenue. Depending on the type of owner you are and your preferences you can choose the avenue for you. Here are the four available avenues:
- Marketplace – In order to sell your business in a marketplace, you will have to prepare data about the business and post the listing. This will generate interest from various buyers. The most common marketplaces where similar companies are listed are BizBuySell and BizQuest. This is a good avenue for those that have a bit of experience in the sales process. If you do not have the required knowledge, this is not the choice for you.
- Auction – By choosing this option you automatically solve half the problems that you would have faced in the marketplace. An auction allows the seller to show the listing to a wide variety of audience at a specific time. Most domains and businesses that are worth $5,000 are regularly sold on auction sites. An auction will be the option for you if you have a small business and are also ok with a lower valuation of it. Also, you can sell it to the highest bidder.
- Broker – The best and safest bet you can make is to choose to sell your SaaS company through a broker. This is for those that have a business that is worth more than $20,000 and requires professional assistance during this process. An expert can help you get the best value for your business. A good broker should facilitate the entire process from start to end. He can also assist you in determining the accurate value of the business. It is recommended to use a broker in case you are not experienced and need help. Additionally, this option will most likely result in a higher price for your business. Depending on the business size, a broker can take up to 3 to 6 weeks.
- Direct – The last option that an owner can choose is to directly sell it by himself. This can be done by utilizing your network, making calls and emails to other people interested in the business. If you are experienced and have a good network, it will be easy for you to find a potential buyer that is willing to give you the price you want.
Ready to value your SaaS company?
To find a value for your SaaS company, saas valuation multiples are essential as they all contribute to the valuation. Once you evaluate your SaaS company, the next step will be your sale options and exit strategy. It is best to involve a professional broker to give you a good idea of your company’s worth. They will accurately calculate the SDE profit and advise based on the previous transactions and the business assessment.
A good broker will use tools to assist him in calculating and determining the value of your business, one such handy tool is Eqvista. Eqvista is software that provides you with all the necessary tools that you need in evaluating a business, creating a cap table, and managing shares. Learn more about our 409a valuation services!
Interested in issuing & managing shares?
If you want to start issuing and managing shares, Try out our Eqvista App, it is free and all online!
