409a Valuation in United Kingdom
In this article, we explain what a 409A valuation is, when you need one, and whether or not your company should get a 409A valuation in the UK.
The United Kingdom is one of the most popular countries for U.S. companies to establish their presence in Europe. According to the World Bank Group, the UK has the world’s fifth-largest economy and the European Union’s second-largest economy. It’s no surprise that many entrepreneurs want to expand their company to the UK.
UK Companies in the US
The UK market is the largest in Europe and the fifth-largest in the world for US goods exports. It is highly developed, sophisticated, and diversified. The United Kingdom is the world’s largest market for service exports from the United States. It is highly developed, sophisticated, and diversified. Aerospace Products, Agricultural Products, Cyber Security, Medical Equipment, New Build Civil Nuclear, some consumer items (such as Pet Products), Smart Grids, Sustainable Construction, and Travel & Tourism are all significant sectors of US exports.
Overview of the UK companies and business with the US
The United Kingdom has significant trading linkages with most countries in the world due to its history; it is geographically located in Europe and serves as a time zone bridge between the United States. The United Kingdom is the second-easiest country in the European Union to start and run a business (after Denmark) and the seventh-easiest jurisdiction internationally. This is owing to its sophisticated but modern legal system, stable political climate, and pragmatic attitude to commercial regulation.
Important US tax issues to know
- 83(b) election – The Internal Revenue Code’s (IRC) 83(b) election allows an employee or startup founder to pay taxes on the complete fair market value of restricted shares at the time of grant. The 83(b) election is for equities that have a vesting period. The 83(b) election instructs the IRS to tax the elector for stock ownership at the time of gift rather than when the stock vests.
- ASC 718 – Employee stock-based compensation is expensed on an income statement in accordance with ASC 718. Equity awards are a type of compensation that is subject to a set of accounting regulations known as ASC 718 that corporations must adhere to. Expense accounting was previously known as FAS 123(r), but it is now governed by ASC 718.
- ISO 100k – In contrast to Non-qualified Stock Options (NSOs or NQSOs), Incentive Stock Options (ISOs) receive preferential IRS treatment. The key advantage is that when the option is exercised, the spread between the fair market value (FMV) and the initial exercise strike price is not subject to ordinary income tax. Ordinary income tax is withheld on the spread by NSOs at the time of exercise. ISOs, on the other hand, are nevertheless subject to the Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) in order to prevent affluent persons from hiding all of their income in this method. Another IRS rule designed to prevent the ISO program from being utilized as a tax shelter is the $100K Limit (100K ISO Limit).
- Form 3921 & 3922 – The IRS has issued two forms (and instructions) for reporting ISO workouts and ESPP share purchases: Form 3921 for ISO exercises and Form 3922 for ESPP share purchases. For each workout or purchase made during the calendar year, a new form must be completed and filed. As an example, if an employee used many ISO awards over the course of a year, in a calendar year, the employee must receive a copy of Form 3921 for each exercise, and the corporation must receive a copy of Form 3921 for each exercise, will be required to file numerous tax returns with the IRS.
- Internal Revenue Code Section 409A – A 409A is an impartial evaluation of a private company’s common stock, or equity reserved for founders and workers, at fair market value (FMV). It is used to calculate the fair market value (FMV) of your company’s common stock which a third-party valuation firm usually does. The cost of purchasing a share is determined by this valuation.
409a Valuation & UK Companies
Each company must get a 409a valuation to ensure that they don’t end up paying the penalties. UK Companies have a different approach for getting the 409a valuation. Their valuation is often audited only by the expert entities and their taxation is based upon certain norms which might make it difficult for companies to get the 409a valuation.
What is a 409a valuation?
A 409a valuation is an assessment of a private company’s stock and determines the fair market value (FMV) of that company. Unlike public firms, private companies have no share prices available to examine at any time. Private companies that want to issue shares to their employees must have them assessed. This is where the 409A valuation comes in.
409A valuations should be done annually or if the company has a material event, such as new financing, to take advantage of the IRS safe harbor (i.e., not be subject to certain IRS fines).
When is a 409a valuation required for a UK company?
A 409a valuation is required by the company when it doesn’t know the value of the stock. For example, If you want to sell a table but don’t know how much it’s worth, you sell it to anyone. Using the same analogy, a 409a becomes vitally important if a firm intends to offer equity. It’s impossible to sell shares if you don’t know how much they’re worth. A 409a valuation is required if your company is:
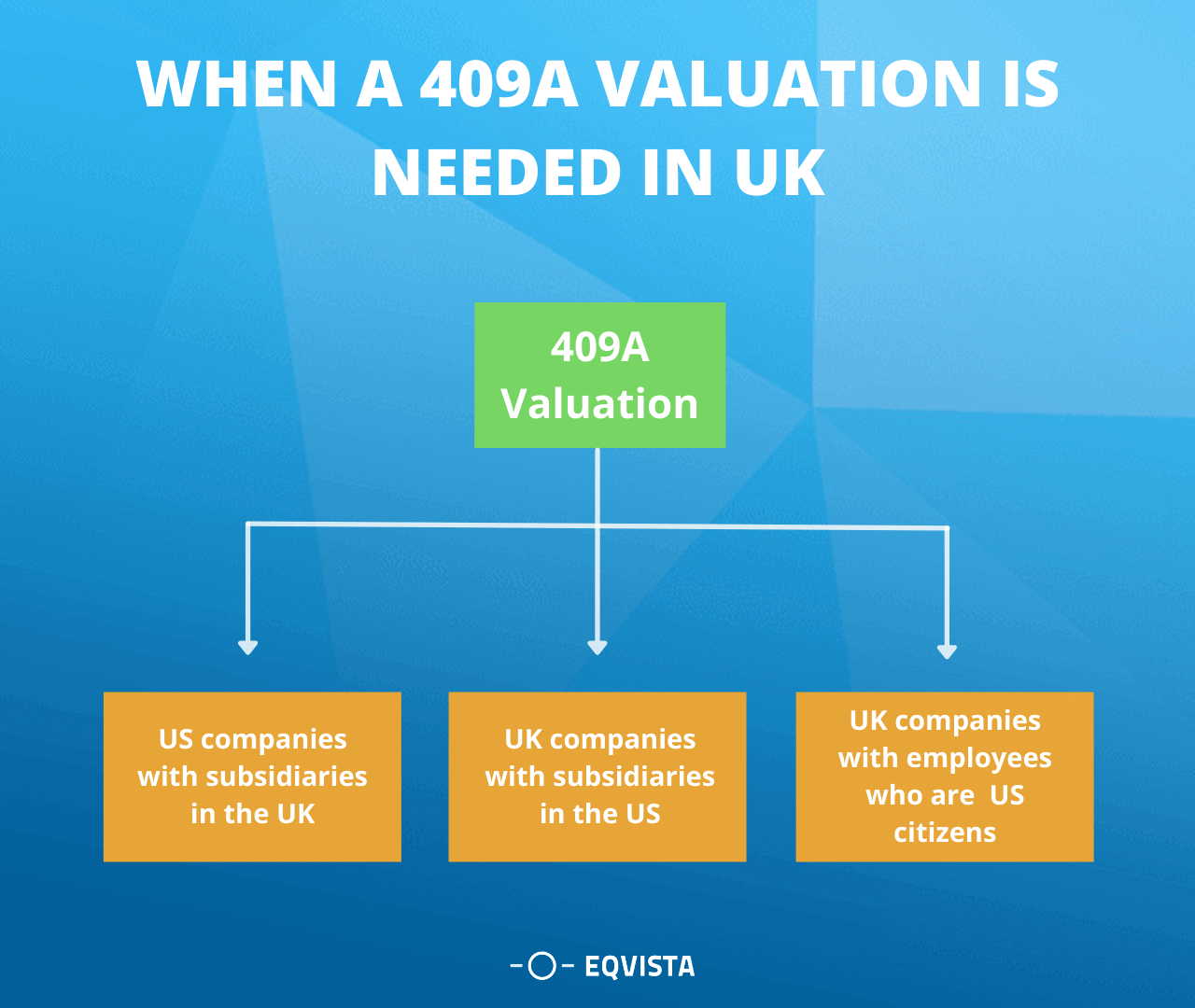
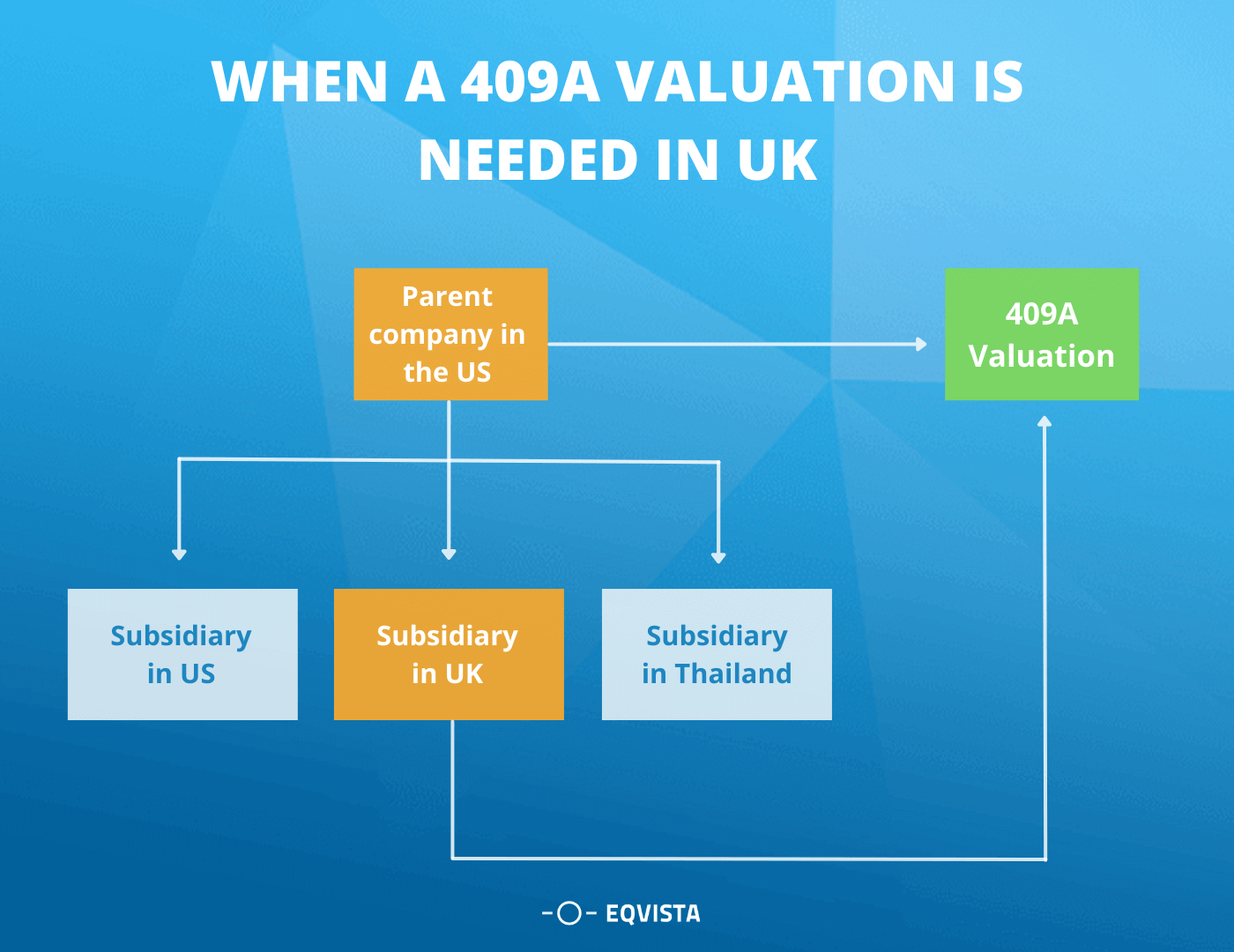
US Holding company with the UK subsidiaries
A holding company is an entity which is associated with a corporation or a limited liability company. It is used to perform certain operations which are not related to any kind of buying and selling of products and services. It’s main function is to provide the membership interests in different firms and take the charge of those companies.
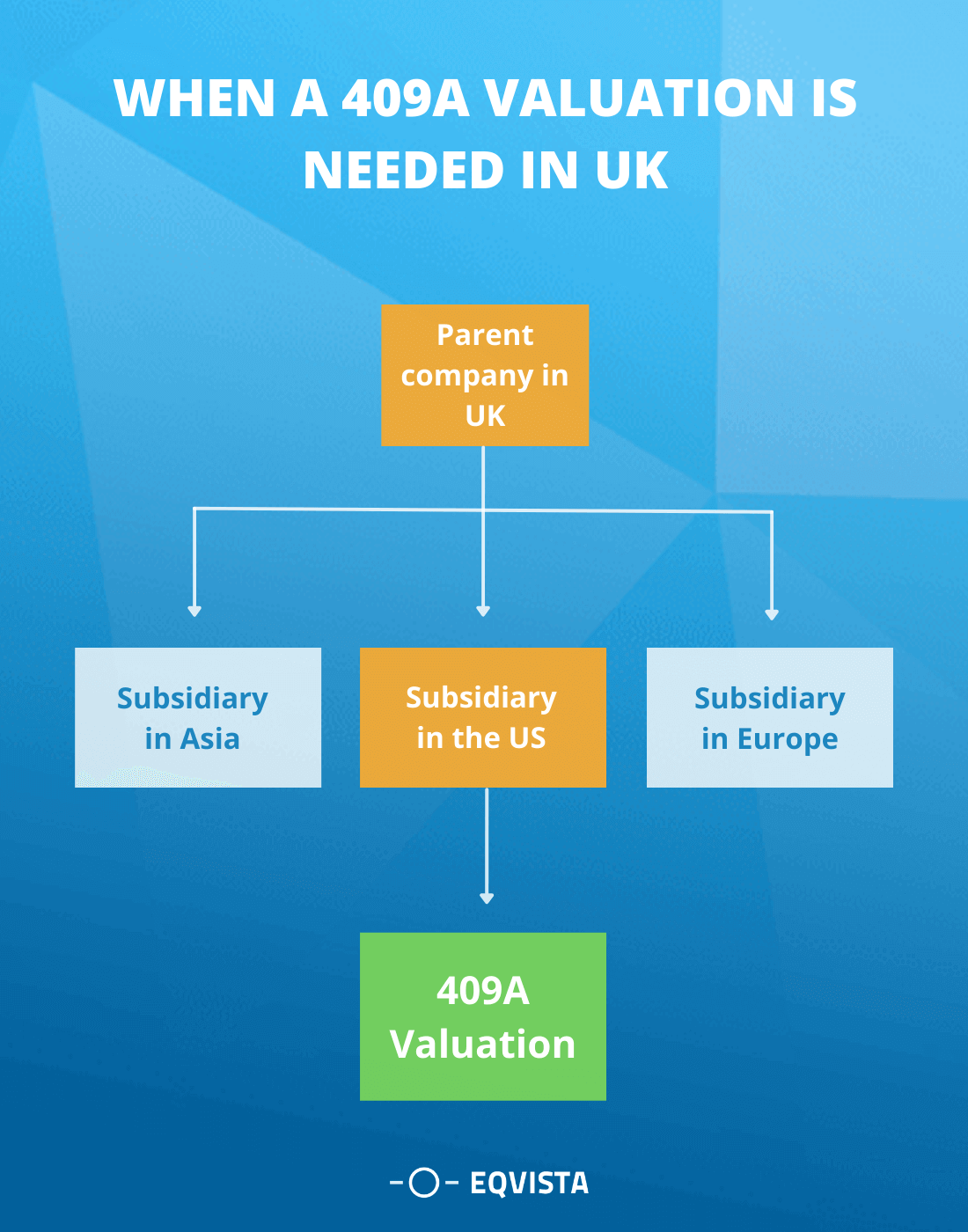
UK Holding company with US subsidiaries
Employee share plans have long been a feature of the remuneration packages offered to employees of UK-listed companies. Employers can offer stock plans to all employees (all-employee plans) or to senior executives and executive directors on a case-by-case basis. ESOP in the UK Companies are based on some bylaws, which are followed by ESOP in the UK.
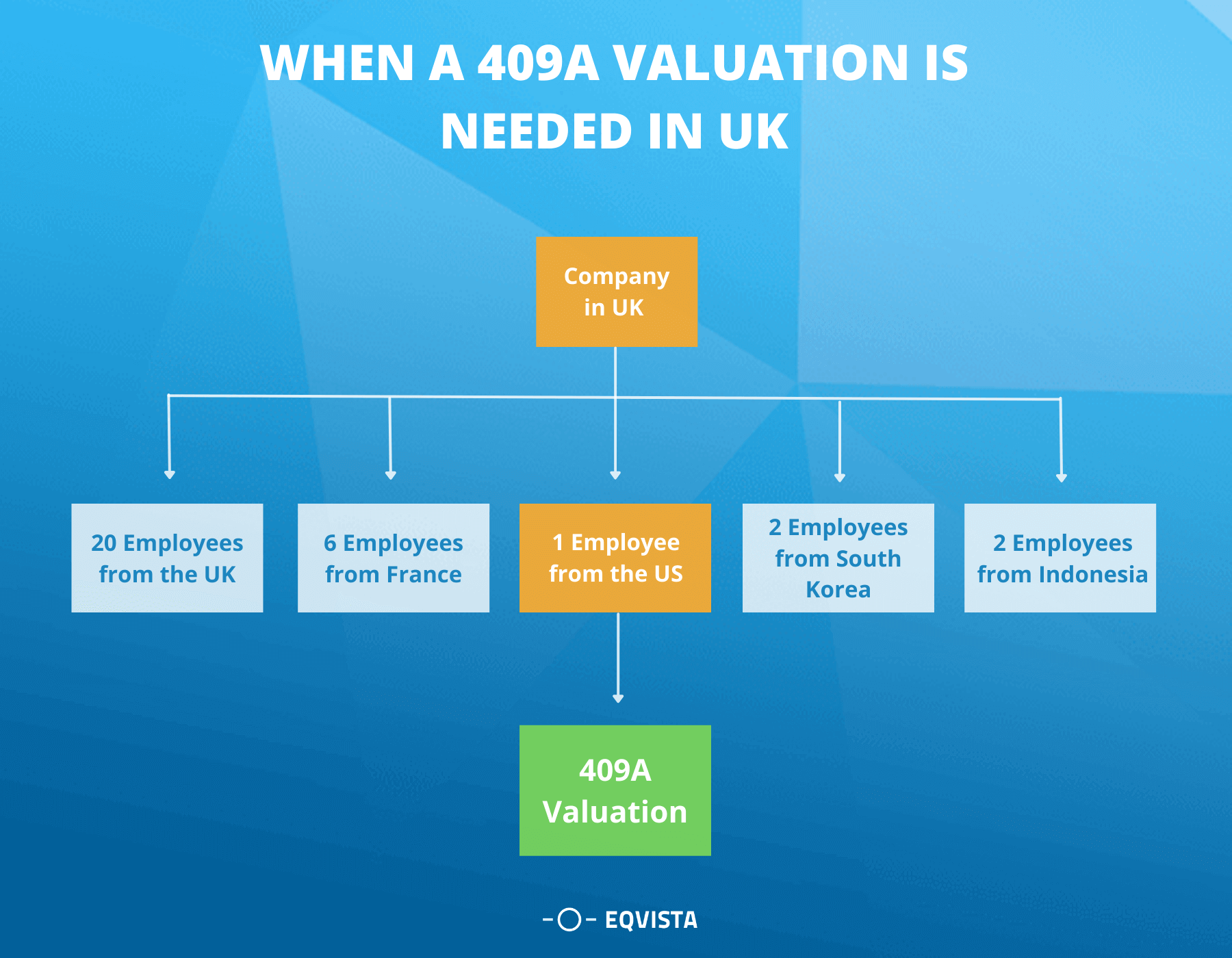
UK companies with US employees (Offering ESOPs/Other Incentive Programs)
Employee ownership can be achieved in a number of different ways. Employees can purchase the stock outright, receive stock as a bonus, earn stock options, or participate in a profit-sharing arrangement. Employee cooperatives, in which everyone has an equal vote, allow certain employees to become owners. The ESOP in the UK companies or employee stock ownership plan, is by far the most frequent type of employee ownership in the United States. These tax benefits, as appealing as they are, are not without limitations and consequences. ESOPs in the UK Companies are not permitted in partnerships or most professional corporations under the law. S businesses can use ESOPs in the UK Companies however, they are not eligible for the rollover approach outlined above and have lower contribution limitations. Private corporations are required to repurchase the shares of retiring employees, which can be a significant expense.
Other situations for 409a valuation
A third-party valuation provider is often employed to estimate the fair market value (FMV) of your company’s common shares under 409A in the UK. The strike price for options granted to employees, contractors, advisors, and anyone else who receives common stock is determined by 409As. When two countries do a stock exchange there might be some situations that may occur.
- UK employee share option plans (SAYE, EMI, CSOP, Nontax favoured share option plan) – Employee share plans have long been a feature of the remuneration packages offered to employees of UK-listed companies. Employers can provide stock plans for all employees (all-employee plans) or to senior executives and executive directors on a case-by-case basis.
- SAYE – Employers can provide employees with share options on a tax-favored basis through a save-as-you-earn (SAYE) program. Employees agree to save a set amount over a set length of time, after which their savings may be eligible for a tax-free incentive in certain conditions.
- EMI – Smaller trading organizations that award share options to chosen employees can benefit from Enterprise Management Incentive (EMI) options, which provide significant tax benefits. EU state assistance authorization is also required for EMI choices.
- CSOP – An employer can provide employees the option to buy a certain number of shares at a certain price and within a certain time frame through a corporate share option plan (CSOP). Options are usually granted at a price equal to the market value of the shares at the time of award (they cannot be granted at a lower price) and are usually not exercisable for three years after the grant.
- Non tax favored share option plan – When an option is exercised, the difference between the market value of the shares on the date of exercise and the exercise price is taxed. If the shares match the required criteria, the employer must account for income tax. If the employer is liable, it must pay income tax, employee NICs, and employer NICs through PAYE. The liability is recouped in the same way as EMI is recouped.
- HMRC shares and asset valuation – The value of acquired tangible, intangible, and intellectual property assets, as well as liabilities such as deferred revenue and contingent consideration, must be reset to fair value in a purchase price allocation (PPA) report after a business combination or the acquisition of a collection of assets. Considered deals and pre-completion valuation assistance help potential acquirers understand the acquisition’s potential accounting implications.
Why is a 409a valuation important?
Defining the fair market value of shares
A fair market value of shares is defined as the value that is being calculated based upon investments made by the shareholders and it also tells about the market value as well. Because preferred stock is given to investors, a post-money valuation is based on preferred stock price, but a 409A is based on the common stock price. Preferred stock is frequently more valuable than regular stock due to particular characteristics.
Fair value of company
A 409A is used to calculate the fair market value (FMV) of your company’s common stock, which a third-party valuation firm usually does. The strike price for options granted to employees, contractors, advisors, and anyone else who receives common stock is determined by 409As.
While companies frequently conduct their financial analysis to estimate FMV early in its lifespan, valuations grow more complicated as time goes on, requiring more knowledge and taking longer.
Safe harbor status
When it comes to valuing private shares, the 409A provides a structure for private corporations to follow. When an unaffiliated or independent party does the valuation, it creates a safe harbour, which means the IRS will assume the 409A is “reasonable”—with a few exceptions.
Consequences for not complying with 409a while issuing equity
An independent company valuation is necessary for nonqualified deferred compensation (NQDC) plans that contain stock options and/or stock appreciation rights (SARs). The valuation determines the strike price at which the opportunities and SARs can be exercised.
The penalties of not complying with 409a can be severe for the company and the employees too. The sanctions will ruin your staff before they ruin your firm, but you can bet the two will happen in quick succession.
Tax penalties
Noncompliance with section 409A can result in the following tax penalties for employees:
- Even if payment is made in the following years, employees must pay income tax and a 20% penalty on any deferred vested amounts under the NQDC plan as of the last day of the vesting year.
- Employees must pay a premium interest tax of 1% above the federal underpayment penalty rate on failed compensation from the vesting date forward. Employees may be required to pay additional penalties as a result of understating their income. Employees may also be subject to penalties imposed by the state.
Common Valuation Methods
The common valuation methods are those that their companies use to calculate and check the stored stock. There are three differences used to analyze the value of the stock and follow the instructions mentioned in the 409a section.
- Asset approach – A company’s net asset value is the emphasis of an asset-based approach to business valuation. Total liabilities are subtracted from total assets to arrive at the net asset value. There is some space for interpretation when determining which of the company’s assets and liabilities to include in the assessment and how to measure their worth. Financial executives have a significant duty in determining and keeping awareness of a company’s value.
- Market approach – The market approach is a method for calculating an asset’s worth based on the selling price of similar assets. Along with the cost technique and discounted cash-flow analysis, it is one of three main valuation methodologies. In circumstances where there is a lot of data on similar transactions, the market method shines. Alternative procedures may be required if that data is not available.
- Income approach – The income technique estimates fair value based on the income generated by the property. The capitalization rate is divided by the net operating income to arrive at this figure. When it comes to business valuation, the income method reigns supreme. The majority of people start a business to make money. As a result, if someone is buying a firm, the amount of money they will generate in the future is the most important consideration in determining the purchase price. In simple terms, the income strategy is analyzing a company’s financial history in order to forecast future earnings.
Calculations for 409A Valuation in the UK
Let’s say there is a company, Daydreamotors Inc., which manufactures automobiles such as cars and motorcycles all over the world. This company has some senior managers and executives who are expats and US citizens, who need to declare tax back in the US for their stock options they plan to exercise in the future. In order to determine the strike price on these options, Daydreamotors Inc. decides to undergo a 409a valuation to find the value, and exercise price, for their ESOPs.
Here is a basic look at their Cap table:
| Security Name | Shares | FD% |
|---|---|---|
| Common Stock | 6,000,000 | 35.82% |
| Preferred Stock | 9,000,000 | 53.73% |
| ESOP | 1,750,000 | 10.45% |
| Total | 16,750,000 |
After having their 409a valuation processed, the resulting value was calculated as:
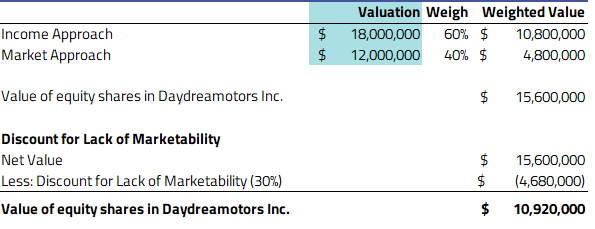
With the total valuation of the company at $10,920,000 after the DLOM, and capital structure with 16,750,000 shares, after processing the value through a waterfall analysis, the final share price was calculated as:
$0.46 price per share
With this, Daydreamotors Inc. was able to issue its stock options according to its ESOP plan at a strike price of $0.46 to its US staff.
Need a 409a Valuation Report for Your Company?
Get a 409A valuation for your company in the UK with Eqvista! Our highly experienced valuation analysts will guide you through the whole process: from getting your information to sharing updates. Reach out to learn more on how to get your 409A valuation.
Interested in issuing & managing shares?
If you want to start issuing and managing shares, Try out our Eqvista App, it is free and all online!
