Understanding the IRS Filing Process
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) is a federal organization responsible for enforcing tax laws and collecting taxes from people and corporations in the United States. Founded in 1862, it administers other types of taxation outside income tax, including gift, excise, and inheritance. The Internal Revenue Service often performs audits to check for tax compliance and IRS filing. It involves filling out any necessary paperwork and timetables.
This article aims to educate you on avoiding common IRS filing mistakes and some practical tips for successful IRS filing.
IRS filing process
The IRS is the government organization responsible for collecting federal taxes from individuals and businesses in the United States. As a branch of the U.S. Treasury Department, the IRS ensures that the Treasury Secretary’s duties are compliant with the Internal Revenue Code (IRC).
But how does the IRS filing process take place? Why is it important? Let’s understand them in this section.
How does the IRS filing process work?
The IRS aims to enforce tax laws and collect federal revenue from all American taxpayers, including people and businesses. To do this, the organization collects and processes tax returns.
In the words of the organization:
- Tax legislation enacted by the US Congress affects US taxpayers.
- Taxpayers are responsible for knowing and settling their tax liabilities.
- The Internal Revenue Service assists law-abiding taxpayers while enforcing the payment of taxes by those who avoid doing so.
One of the primary functions of the IRS filing process is to process federal tax filings and collect income from individual and business taxpayers. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) provides tax refunds when a person is due one. According to IRS data for the time frame ending February 24, 2023,
- Having collected 45.98 million separate returns
- Having processed 45.72 million tax returns.
- Paying out $108.20 billion to 35.14 million people in refunds
Importance of proper IRS filing process
One of the most important skills you can acquire is filing taxes with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). Here, we’ll discuss why filing taxes with the IRS is vital to your financial health.
- You may minimize your tax liability and save money by making the most of your discounts and tax credits by correctly filing your taxes and claiming all credits and deductions to which you are entitled.
- Maintaining accurate and regular filing will lessen the possibility of an IRS audit, which can be laborious and time-consuming.
- Individuals and corporations may save time and money by learning about and following the IRS filing process. It aids in fiscal resource management by making tax obligations more transparent.
- Maintaining credibility in the banking sector requires accurate tax reporting. The capacity to get loans, sign contracts, and gain banks’ confidence all depend on your reputation.
- Accurate tax reporting is important because it helps the government allocate resources and pay for essential services. Proper tax filing guarantees a fair allocation of funds that support public services and infrastructure.
Business Tax Filing Types
Considering a company’s legal structure in the IRS filing process is essential. Here’s a rundown of how various company structures commonly approach tax reporting:
Sole Proprietorship
A solitary proprietorship consists of no more than the business owners themselves and no more. Owners of businesses must file individual tax returns (Form 1040) to account for their business’ revenue and expenditures.
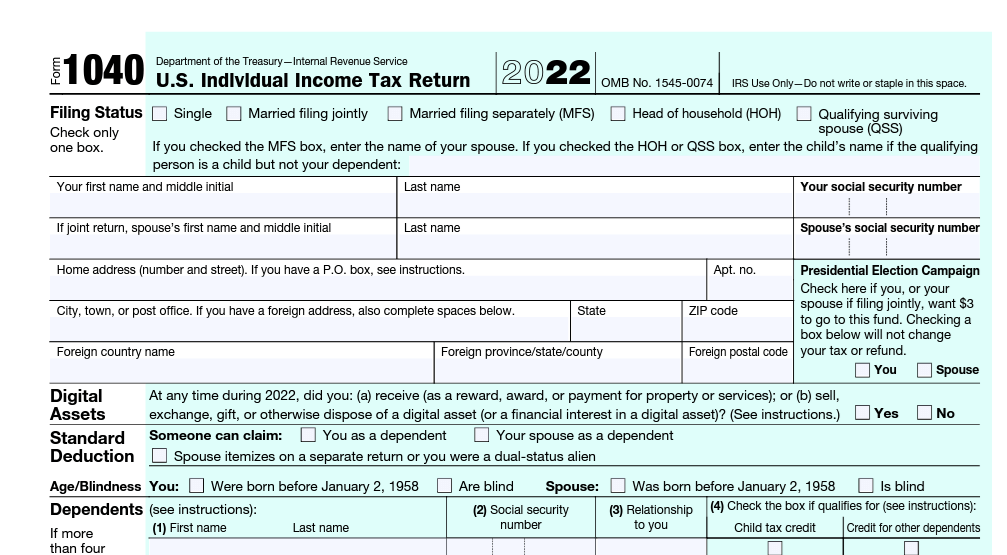
One often uses Schedule C or Schedule C-EZ to record business income and deductions. The business’s tax obligations are the exclusive responsibility of the owner.
Partnership
Since it operates as a distinct business, a partnership is exempt from its income tax. The company completes a tax return (Form 1065) each year to detail its financial transactions.
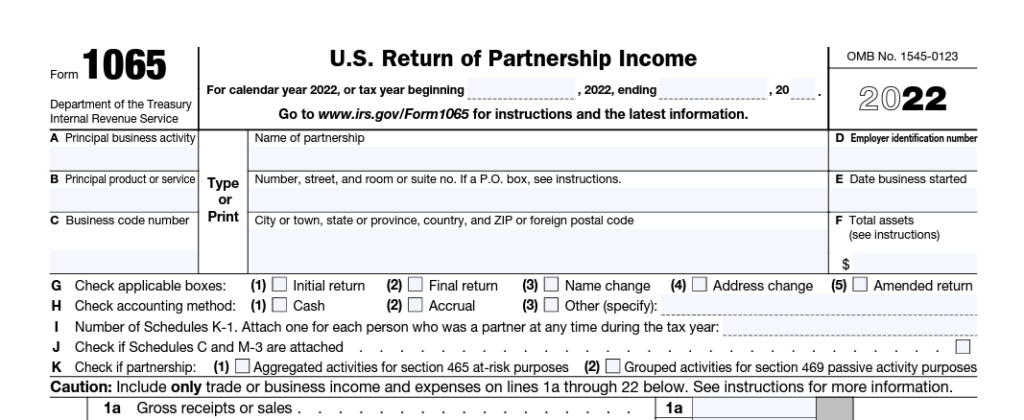
Each partner gets a Schedule K-1 outlining their portion of partnership revenue and expenses. Individual tax filings are where partners disclose this information.
Corporation (C-Corp)
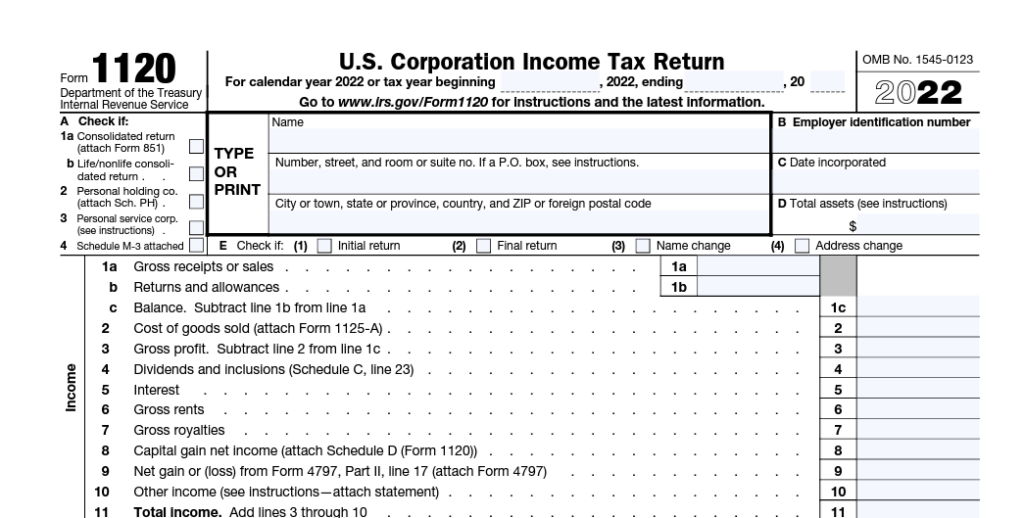
In law, a C company exists independently of its shareholders. Using IRS Form 1120, it submits its corporation tax return. Taxes on company profits must comply with the applicable rates. Investors must report and pay taxes on dividends received from a company.
S Corporation (S-Corp)
Regarding taxes, a S company is similar to a C corporation in that it is a distinct organization. The company reports its revenue and costs on Form 1120S, which it submits. Shareholders’ tax returns will reflect any profits or losses distributed to them.
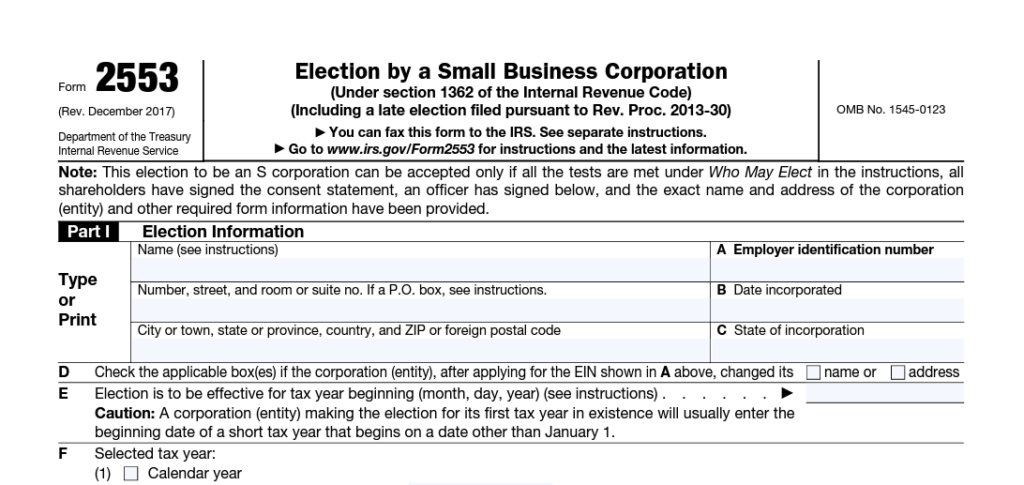
This setup prevents the company and its employees from being taxed twice.
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
A limited liability company may choose its tax treatment. To calculate taxes, it might be a sole proprietorship, partnership, S corporation, or C corporation. The Internal Revenue Service does not treat LLCs as a separate tax entity.
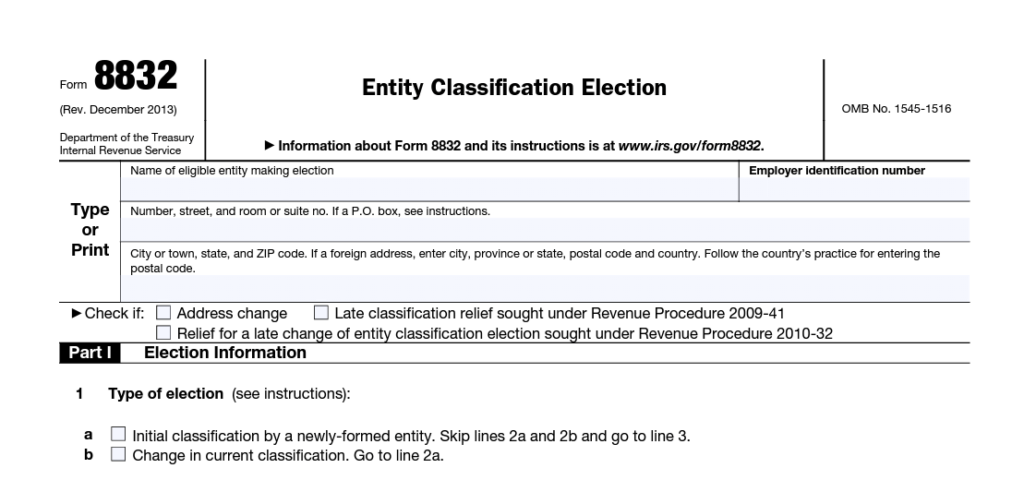
The LLC’s election and the functions of its members determine the tax treatment.
International Business
International Compliance aims to enhance the efficient and effective use of resources to strengthen taxpayer compliance. LB&I’s objective is to improve the selection of returns, identify issues associated with non-compliance risk, and optimize the utilization of limited resources.
Other IRS Filing Options
Additional IRS filing process alternatives exist for unique circumstances and companies outside the general business tax filing options.
To better understand these supplementary IRS forms, consider the following:
- Estate and Gift Tax- A person’s estate may be subject to a tax after they pass away. The transfer of assets between living individuals is subject to gift tax. The executor of an estate is legally responsible for reporting estate assets and determining estate tax obligations by filing Form 706 (Estate Tax Return). Significant lifetime gift-givers may need to submit IRS Form 709 (Gift Tax Return).
- Nonprofit Organizations- 501(c)(3) organizations and similar nonprofits are exempt from paying taxes. These organizations typically submit a yearly information return on Form 990 or Form 990-EZ to keep their tax-exempt status and disclose their financial operations. By filing these reports, the organization lets the IRS and the public in on its financials and activities.
- Trust Tax Filing- It’s important to note that both revocable and irrevocable trusts stand independently as legal organizations. During the IRS filing process in the United States, trusts often use Form 1041 (United States Income Tax Return for Estates and Trusts) to disclose taxable income, expenses, and credits. Individuals who receive income from a trust may obtain a Schedule K-1 that specifies their income.
- Foreign Taxpayers- Any non-U.S. resident who has earned money in the United States may be subject to additional reporting obligations. Form 1040-NR or 1040 is the standard U.S. tax return for individuals who are tax residents of a country other than the United States.
For example, international firms in the United States may need to submit Form 1120-F with the Internal Revenue Service.
Steps involved in the IRS filing process
There are several critical measures you must take when submitting your taxes with the IRS to guarantee the accuracy and promptness of your submission.

The main procedures in the IRS filing process are as follows:
- Gather Necessary Documents and Information- Gather your tax returns (both federal and state), W-2s, 1099s, receipts, and other financial papers (such as records of income, spending, and deductions).
- Choose the Correct Filing Status- When preparing your taxes, choose the proper filing status, such as single, married, filing jointly, or head of household. This status directly affects your tax liability and eligibility for certain deductions and credits, making it essential to accurately reflect your personal and family situation.
- Calculate Total Income- Determining your entire income before proceeding with your tax return is essential. It includes money received from working a job, money received from running a business, money received from investments, and money received from any other source.
- Claim Deductions and Credits- Find all the deductions and credits you can to help you pay less in taxes. Interest on mortgages, student loans, and retirement accounts are standard deductions. Obtaining a tax credit, such as a Child or Earned Income Tax Credit, may result in significant tax reductions.
- Complete the Tax Forms- Choose the proper tax form to file your taxes correctly. Include any additional documents and schedules required to provide a complete accounting of your revenue and expenses.
- Calculate Taxes Owed or Refund Due- You can determine how much tax you owe by multiplying your taxable income by the applicable tax rate(s). Find out whether you owe money to the government or if you may expect a refund by comparing this to your total tax payments and credits.
- File the Tax Return- You may submit your tax return to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) electronically by utilizing tax preparation software, an IRS-approved e-file provider, or by sending in a paper return. Make sure you file by the deadline.
- Review and Submit- Check your calculations and ensure you have included all the necessary information by carefully reviewing your tax return. Inaccuracies or omissions may cause fines or additional waiting time.
IRS forms and Documentation
You may need to fill out one of these IRS forms during the IRS filing process:
Form 1065: Partnership Tax Return
Partnerships disclose their financial activities on Form 1065, including income, deductions, profits, and losses. Partnerships are exempt from paying their income taxes because they are “pass-through” companies.
The money “passes through” to the partners’ accounts. The partnership’s revenue and deductions get distributed to the partners on Schedule K-1. They need this data to accurately report their portion of the partnership’s revenue on their tax returns (Form 1040).
Form 1120: Corporate tax return
Companies, distinct entities from their shareholders, file their taxes using Form 1120. As a general rule, shareholders of C companies are not directly responsible for the business’s tax obligations, paid by the firm based on its net income.
Businesses must detail their earnings, expenses, credits, and deductions on this form. The IRS filing process determines the company’s tax obligation with this data.
Form 1120S: S Corporation tax return
S companies file their taxes using Form 1120S and are distinct legal entities that benefit from pass-through taxation. The federal government does not tax the profits of S businesses.
To file their tax returns (Form 1040), S corporation shareholders get a Schedule K-1 that details their portion of the company’s income and deductions.
Form 940: Employer’s Annual Federal Unemployment (FUTA) Tax Return
Companies record and pay federal unemployment taxes (FUTA) using Form 940.
The FUTA tax helps pay employees unemployment benefits when they lose their jobs. Employers with a specified payroll must complete this form yearly to fund federal unemployment benefits.
Employees must properly report and pay their FUTA tax to get unemployment benefits.
Required Documentation for IRS Filing
Make sure you have the following necessary documents when you are ready to file with the IRS:
Personal Information
Gathering your personal information is the first step in the IRS filing process. Accurate and up-to-date information about you, your spouse, and your dependents is essential for a trouble-free tax filing experience.
Income Documentation
It is crucial to disclose your income when submitting your taxes accurately. To fully understand your financial condition, you must compile some documentation.
You should collect the following:
- Earnings and tax withholding statements (W-2) from your employer.
- 1099 forms for numerous income streams, such as interest, dividends, and self-employment.
- Bank statements with details about your money transactions.
- Investment ledgers to record gains or losses.
Deduction Records
You may considerably lower your taxable income by taking advantage of deductions, but only if you keep accurate records. Take the following into account when calculating deductions during the IRS filing process:
- Essential documents for deducting mortgage interest like mortgage interest statements.
- Documentation and receipts for all healthcare-related costs, including premiums.
- Donation documentation, such as receipts and acknowledgments from approved charities.
Tax Credits Documentation
Although tax credits may significantly reduce your tax bill, you must prove your eligibility to get one. Information needed for various tax deductions includes the following:
- Educational costs record, such as tuition and loan interest, to claim a tax credit.
- Proof of childcare expenses, such as invoices, to claim the Child and Dependent Care Credit.
Common mistakes to avoid in the IRS filing process
Knowing the most prevalent pitfalls and taking precautions to avoid them is essential while navigating the IRS filing process. Consider the following potential pitfalls:
- Filing Status Errors– Choosing the wrong filing status might have serious consequences. To qualify as the “Head of Household” for someone, you need to satisfy specific requirements, such as covering more than half of the monthly mortgage or rent payment.
- Mathematical Errors and Incorrect Calculations- Mathematical mistakes may vary from those using basic arithmetic operations to those involving more complicated procedures like calculating adjustments or credits. Avoid disparities by being careful with your computations; the IRS double-checks everything.
- Missed or Inaccurate Information- You must provide precise and comprehensive details. Underreporting and possible audits may occur if one records only some of their income. It includes income from freelance employment, investments, and rental properties. For accuracy, verify information on tax forms like W-2s and 1099s against your records.
- Neglecting to Sign and Date the Return- Forgetting to include your signature and the date on your return is a regular mistake. The IRS filing process may only accept your return if they verify your identity via your signature. Remember to sign in the right spot and that both spouses must put their names down on a joint return.
- Overlooking Deductions and Credits- Some filers need to claim all the tax breaks to which they are entitled. It includes the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) and credits for higher education expenses. It is possible to maximize your tax savings by keeping meticulous records and working with a tax expert.
- Ignoring Important IRS Notices and Correspondence- If you don’t answer the IRS promptly, you might face growing fines and interest. Pay attention to the IRS; read their communication and reply appropriately to any concerns or queries they may have.
- Missing the Filing Deadline- Penalties and interest on any taxes payable may result from filing without an authorized extension after the deadline. If you need more time to complete your submission, you should know what the deadline is so that you may prepare accordingly.
- Incorrectly Reporting Income- An audit by the Internal Revenue Service might result from underreporting income. Ensure you include all your earnings, including those from freelance work, rental property, dividends, and capital gains.
Get expert help for filing your IRS form
Businesses must have a solid grasp of the filing process to file taxes correctly and follow IRS filing process regulations. It helps you avoid typical mistakes that might result in fines or audits as you negotiate the tax system’s intricacies.
Eqvista is a reliable financial services platform that provides expert guidance to streamline and improve accounting processes. You can simplify the procedure, optimize deductions, and ensure you comply with all IRS regulations using Eqvista’s all-inclusive tax preparation and compliance services.
Our certified valuation experts help personalize your services based on your business requirements. Join the club of 6000+ companies that benefitted from Eqvista’s IRS filing service today!
