How to Find Undervalued Stocks?
The 2025 market crash has turned into a rich lode for value investors. S&P’s decline of 4.6% has accentuated the decline of small-cap stocks to nearly 25%. This can offer a significant upturn when markets rebound. The general wisdom may suggest lapping up undervalued stocks, but true value investing needs a disciplined and systematic approach like Joel Greenblatt’s Magic Formula, which has historically delivered 30% annual returns as a total sum of earnings yield and the return on capital.
This article provides a stepwise approach to identifying undervalued US stocks using cross-statement financial metrics to mark stocks trading below their intrinsic value. This will help the reader identify the best/top undervalued stocks that could outperform the markets.

Undervalued US Stock 2025
According to recent data from Undervalued US Stock 2025 – Yahoo Finance, the market capitalization varies significantly, from micro-cap stocks like Velocity Financial (561.296M) to mega-cap stocks like Berkshire Hathaway (1.114T).
Graph of market cap distribution
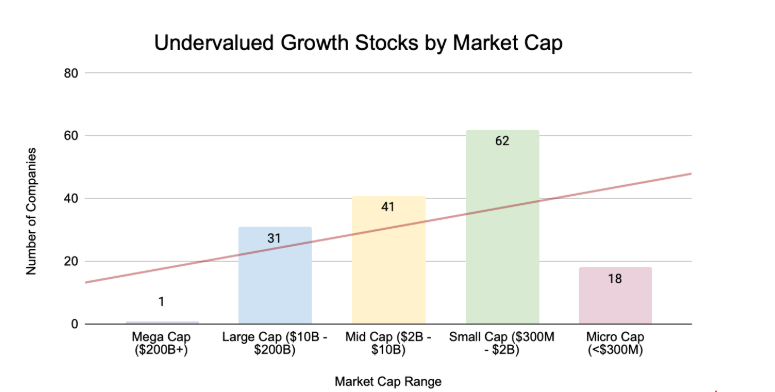
Most undervalued growth stocks fall in the $1B-$5B range, indicating that mid-cap companies are most commonly identified as undervalued. There are relatively few mega-cap companies in this list, suggesting that larger companies are less likely to be significantly undervalued.
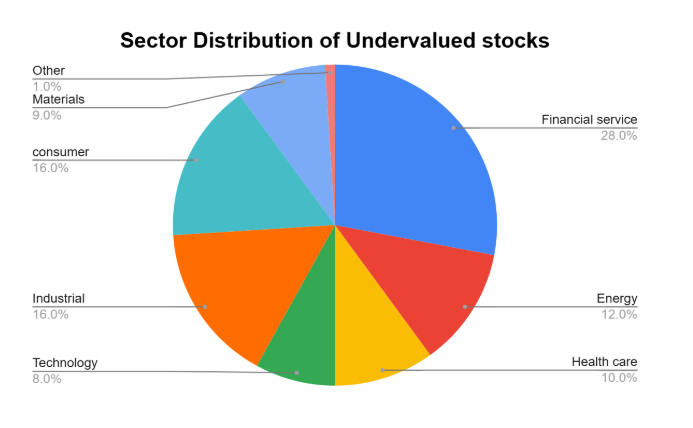
Sector breakdown: Financial Services dominates the list with 28% of all stocks, followed by Industrial and Consumer sectors. This suggests that traditional sectors may currently offer better value opportunities than high-growth technology sectors.
Stock prices vary dramatically from under $5 (EARN at $4.58) to premium-priced stocks like BRK-A ($774,000). The median price point appears in the $15-30 range. Several stocks trading under $10 potentially represent deep-value opportunities.
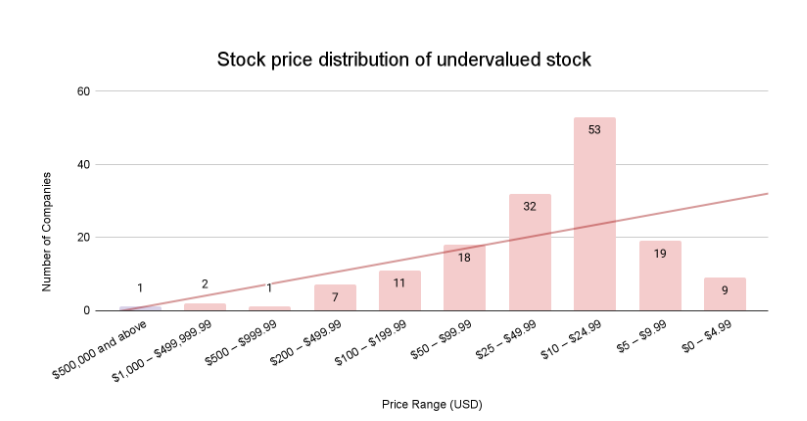
Being classified as “undervalued growth” suggests these companies have the potential for price appreciation. Most stocks are priced between $10-$50, with a significant portion under $10, indicating potential value opportunities. The presence of a few ultra-high-priced stocks (like Berkshire Hathaway) skews the average but doesn’t represent the typical stock in this group.
Key Metrics and Ratios to identify undervalued stocks
Metrics and ratios serve as a quantitative measure to evaluate the quality of stock. Using metrics, analysts know how to identify undervalued stocks. These stocks generally have a higher potential for growth since they tend to rise to their intrinsic value. However, this may not always be the case as the stock market is not always rational. Some of the most widely used metrics include:
Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio: A higher P/E ratio would indicate an overvalued stock, while lower ratios would suggest an undervalued stock. Investing in undervalued stock using a lower P/E ratio can be beneficial, but the value of the P/E ratio that would suggest over- or undervaluation differs from industry to industry.
Assuming a market price of $120 and an EPS of $5, the P/E ratio will be $120 / $5 = 24. Adobe’s P/E ratio is currently 23, which is less than the average tech sector P/E ratio of around 38. A low PE ratio suggests a potential stock price increase.
Price-to-Book (P/B) Ratio: A lower P/B ratio suggests undervaluation while a higher ratio suggests overvaluation. The P/B ratio becomes more relevant for asset-heavy industries, such as real estate or banking.
If a real estate company with equity worth $450 million and outstanding shares of 10 million has a stock price of $120, the book value per share would be $450 million / 10 million = $45. Now, since the stock price is $120, the P/B ratio would be $120 / $45 = 2.67
Enterprise Value to EBITDA (EV/EBITDA): A higher EV/EBITDA ratio means overvaluation, while a lower ratio suggests undervaluation. This ratio is considered more stable because EV and EBITDA are less volatile than the stock price and earnings per share. A company with 7 million total outstanding shares, with the current market price of $8, has a debt value of $10 million and cash of $5 million. The most recent 10-K EBITDA was $7.5 million.
The Enterprise value will be Market Cap + Total Debt – Cash, which is calculated to ($8 * 7 million) + $10 million – $5 million = $61 million. Now, since the EBITDA is $7.5 million, EV/EBITDA will be $61 million / $7.5 million = 8.13. While not a golden rule, several analysts consider EV/EBITDA less than 10 as a robust undervaluation metric, but it needs to be analysed based on industry-specific factors too.
Return on Equity (ROE): A higher ROE with a low P/B may indicate undervaluation as the company uses its assets or equity efficiently., It is always best to use ROE in conjunction with other ratios, especially the P/B ratio. The most recent Apple Inc. Net Income was $93.74 billion and the equity was valued at $56.95 billion. The return on equity was therefore, $93.74 billion / $56.95 billion = 164.61%.
Dividend Yield and Earnings Yield: Dividend yield is the ratio of dividend per share to the price of the share. Earnings yield is the EPS divided by the price of the stock. A higher Earnings yield ratio indicates undervaluation, and a lower ratio indicates overvaluation.
For companies that have zero dividend yield are not profitable and are overvalued. Companies choose not to pay dividends and reinvest are undervalued and the stock is likely to rise. A company with an EPS of $2 and a dividend of $0.75 at a market price per share of $20, will have a dividend yield of $0.75 / $20 = 3.75%. The earnings yield will be $2 / $20 = 10%.
Avoiding Value Traps
Stocks that appear undervalued based on traditional metrics but continue to decline or stagnate because of fundamental problems are Value traps. Here’s how to identify and avoid them:
Check for consistent earnings growth
Regular earnings growth in a company indicates good management and corporate performance. It is measured as the percentage increase in EPS. It is indicative that the operations are smooth and expanding to new markets, increasing market share, and investments are being carried out.
One of the most widely used metrics is the PEG ratio. It is the ratio of the P/E ratio to the growth in EPS. It is a better measure of the stock’s intrinsic value than the standalone P/E ratio and works similarly to the P/E ratio. A higher ratio indicates overvaluation while a lower ratio indicates undervaluation.
Assess competitive advantages
Using financial metrics as quantitative tools to assess a stock’s value is necessary, but analysing the business’s strategic opportunities is equally important.
Let’s take an example of Intel around 2020. The company’s P/E ratio was in the single digits, which suggested a significant undervaluation vis-à-vis the tech sector. However, the company was struggling to introduce newer technology even after spending significantly on R&D. The result was competitors chipping away at the market share and the stock price declining by two-thirds. Intel has lost its competitive advantage to AMD and TSC.
Evaluate financial health and management quality
Financial health can be evaluated using fundamental ratios related to liquidity, solvency, profitability, and operational efficiency. Ratios include currency ratios, interest coverage ratio, debt to equity ratio, profit margin, and other widely used ratios.
Management quality can be evaluated by making sure there is no agency problem, i.e., management working for personal gains. In addition, a higher tenure of top management is a good sign. If there are stock buybacks, this will indicate that the founders are confident about the performance of the company and it’s expected to do well.
Compensation of top management in line with industry standards can also be used as a metric to evaluate management quality.
Determining intrinsic value with Eqvista
Market practitioners are always on the lookout for deviations from the intrinsic valuation. This is not limited to just undervaluation. They can still short the stocks that are overvalued and expected to fall in value in the near future. Successful investing in undervalued stocks requires more than identifying low P/E ratios By focusing on metrics such as EBIT/EV, ROIC, and free cash flow and comparing them against industry peers, investors can uncover stocks trading below their intrinsic value.
As a founder, it is imperative to find out the actual value of your company/stock. Eqvista provides powerful tools to enhance this process:
✔ Advanced screening with real-time financial metrics
✔ Accurate valuation models for both public and private companies
✔ Comprehensive benchmarking against industry standards
✔ 409A-compliant valuations for pre-IPO investments
Our platform helps investors make data-driven decisions by highlighting genuine opportunities while avoiding potential pitfalls in the market.
Contact us today to learn more about our service.
Disclaimer: The information presented in this article about undervalued US stocks is provided for educational and informational purposes only. It does not constitute financial advice, investment advice, or any other type of professional advice. The stock market involves substantial risk, and past performance is not indicative of future results. Readers should conduct their own research and consult with a qualified financial advisor before making investment decisions.

